Long periods of bad weather made 2024 one of the most difficult years for my astrophotography but, I am pleased to say that this, the 11th calendar is another belter! Purchased in 2014, I continue to use a William Optics GT81 telescope for most images taken from home, but this means that I’m running out of suitable targets for this equipment. Part of the answer has been to upgrade related equipment and improve my processing, which I hope you will see reflected in this year’s images. Moreover, I have used new skills and techniques to process the better-quality data in new ways – I hope you like the results?
Below is a brief summary of the calendar images used this year but for other pictures and more detailed information, please refer elsewhere to this website, my Flickr page or Astrobin page. In addtion, a video of the calendar can be viewed HERE on YouTube, which is best accessed on a PC or smart TV screen. The background music this year is from Jean-Michel Jarre’s Oxygène album.
| COVER | ASTRO IMAGING MONTAGE: This colourful splash is a random selection of images, mostly taken from Redhill over the past +10-years of my astrophotography. | |
| JANUARY | SEAGULL NEBULA, IC 2177: Located 3,650 light-years from Earth is the emission and reflection nebula complex of the so-called Seagull Nebula, some 200 light-years in size. It’s been 8-years since imaging this object and for good reason. From my location, the bird flies very low on the southern horizon and thus spends much of its time behind houses, trees, and tall hedges! | |
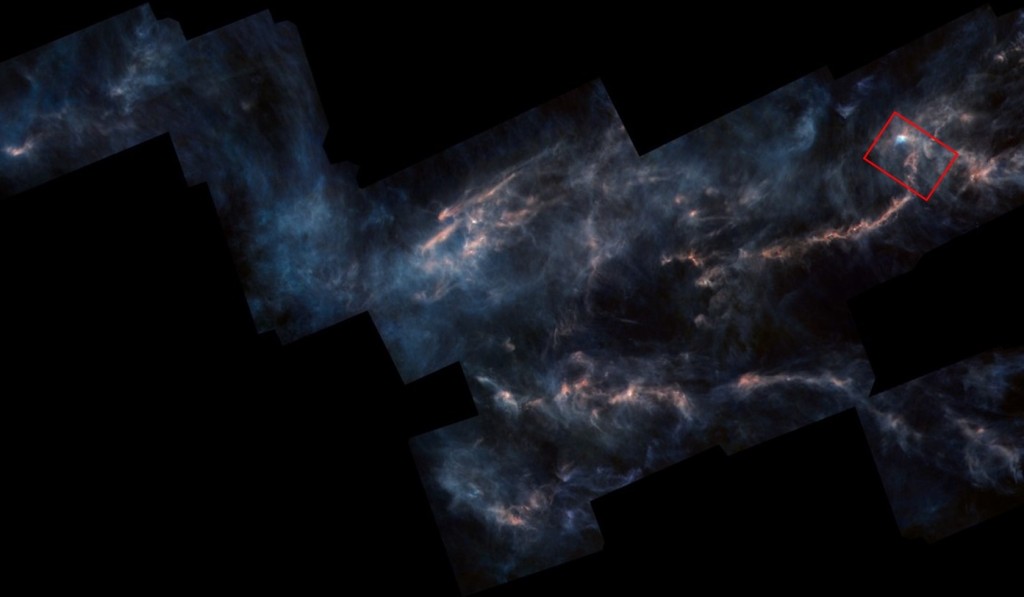
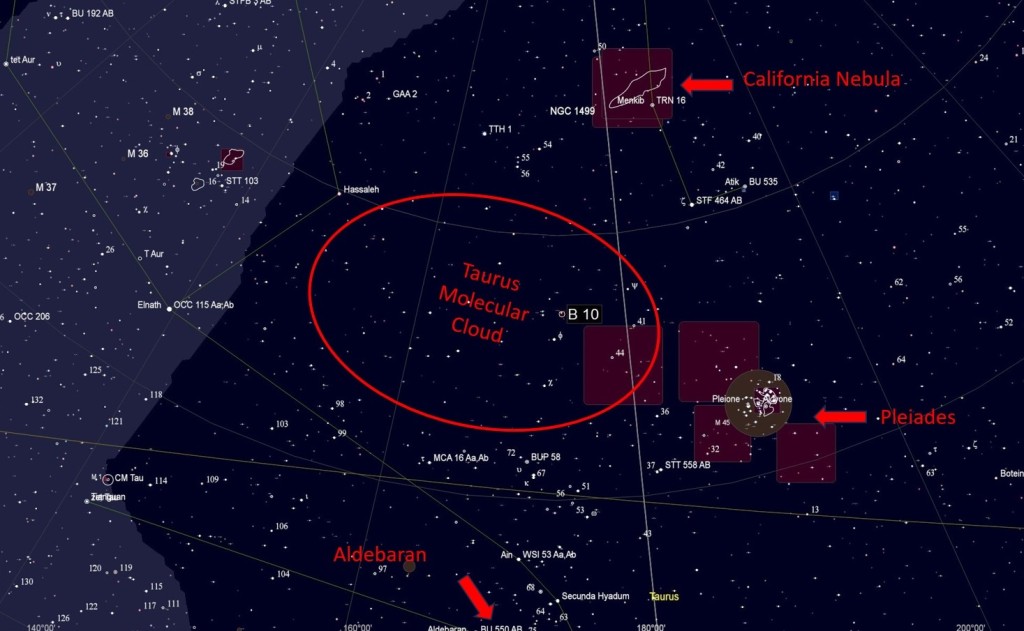
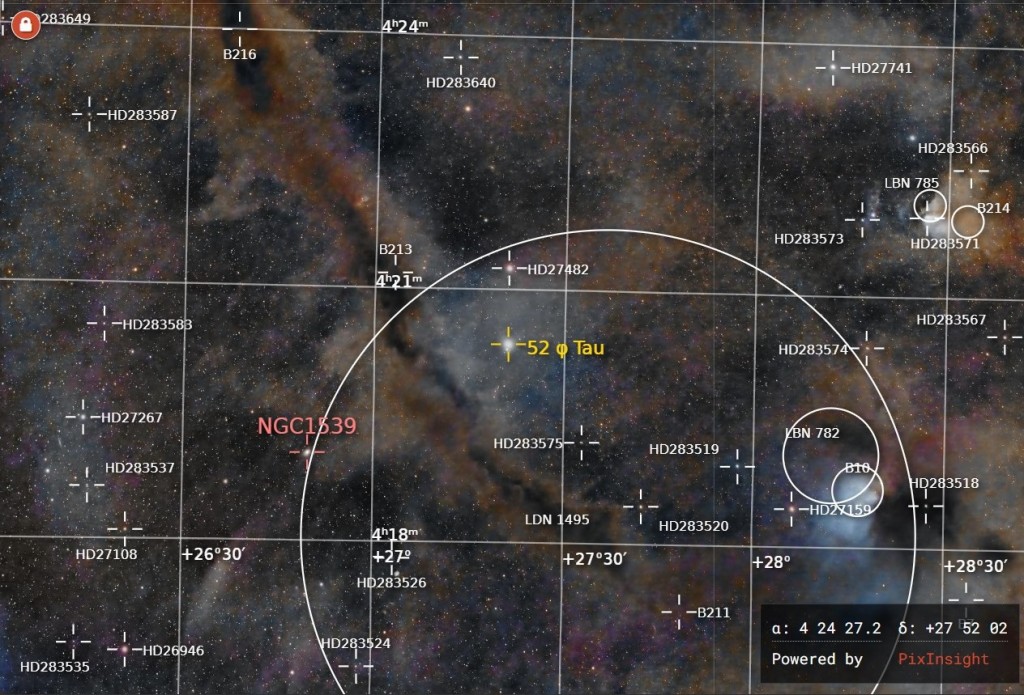
| FEBRUARY | TAURUS MOLECULAR CLOUD: Located northeast of the Pleiades, below (south) the California Nebula (see November), spanning more than 30o of the night sky is the Taurus Molecular Cloud (TMC), a rich area of dark nebulae punctuated by bright areas of new star formation. The TMC is thought to be the nearest star forming region to Earth which, if you look carefully, includes numerous complex dark and reflection nebulae and the odd galaxy. | |
| MARCH | HIND’S VARIABLE NEBULA & HYADES, NGC 1555*: Discovered by the English astronomer John Russell Hind in 1852 this nebula is situated 400 light-years away in the constellation of Taurus, between the stars of Aldebaran and the Pleiades. The nebula is a Herbig-Haro object – a bright patch of nebulosity in which new stars are forming – which often change in apparent size and brightness. | |
| APRIL | LEO GALAXY CLUSTER: With few exceptions, galaxies are located very far from Earth, making them very small from our perspective and a challenge for my equipment. However, here I imaged the spectacular Leo Galaxy Cluster, a mere 330 million light-years from Earth. Containing at least 70 major galaxies, the Leo Cluster unusually consists mostly of spiral galaxies. The bright elliptical galaxy near the centre of the image, has one of the largest known black holes in the universe, which is about 10 billion times more massive than our sun! | |
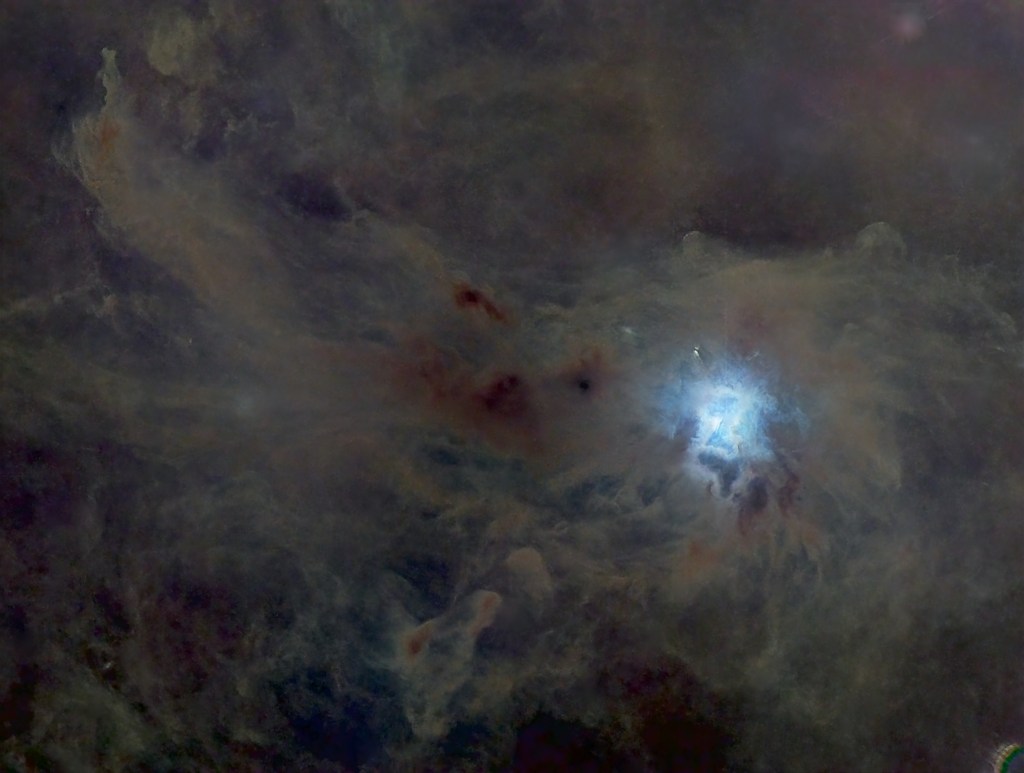
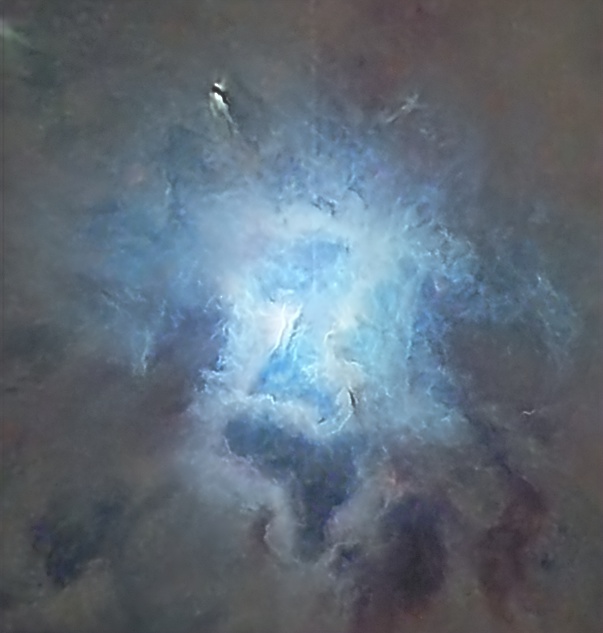
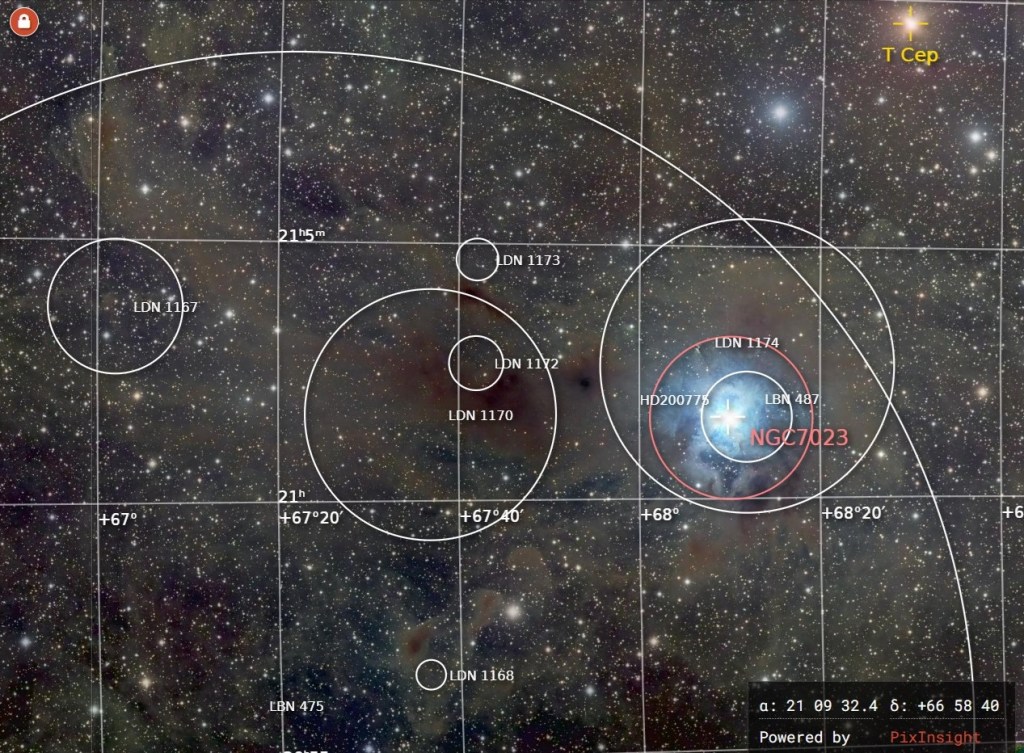
| MAY | IRIS NEBULA, NGC 7023*: While the focus of the image is the alluring bright blue reflection nebula, careful processing reveals that this celestial flower is enveloped within a vast region of interstellar dust. | |
| JUNE | SOMBRERO GALAXY, MESSIER 104: Seen from Redhill, the Sombrero galaxy is even lower in the summer sky than the aforesaid Seagull, transiting between the trees and along the top of our +15-foot hedge! An unbarred galaxy, its bright bulbous centre is encircled by dark dust lanes, which viewed side-on from Earth creates the appearance of a sombrero hat or perhaps a flying saucer? | |
| JULY | PuWe-1*: Is a very faint planetary nebula in the Lynx constellation, discovered in 1980 by Purgathofer & Weinberger. It is one of the largest planetary nebulae visible, with a diameter like the full moon and at 1,200 light-years, is one of the closest to Earth. A planetary nebula is a region of cosmic gas and dust formed from the cast-off outer layers of a dying star; despite the name, planetary nebulae have nothing to do with planets. | |
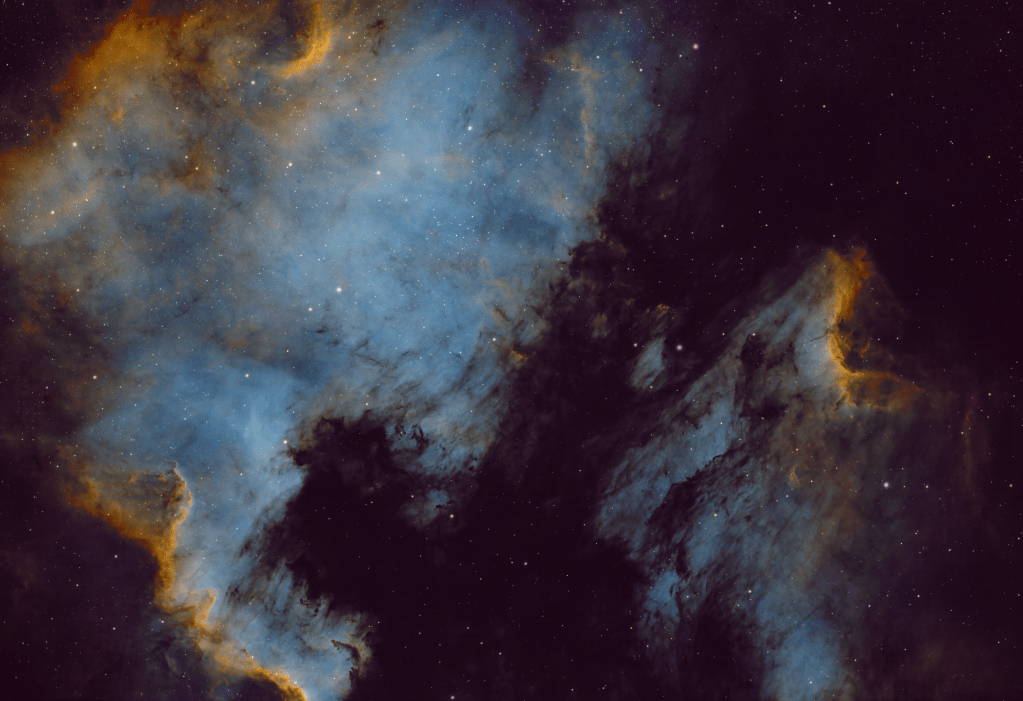
| AUGUST | NORTH AMERICA & PELICAN NEBULAE: It’s at this time of the year (August) I usually turn my attention to the Cygnus constellation and the plethora of imaging opportunities it provides, which inevitably tend to be narrowband targets. Interstellar dust illuminated by large bright areas of star formation are responsible for the formation of both these popular objects. | |
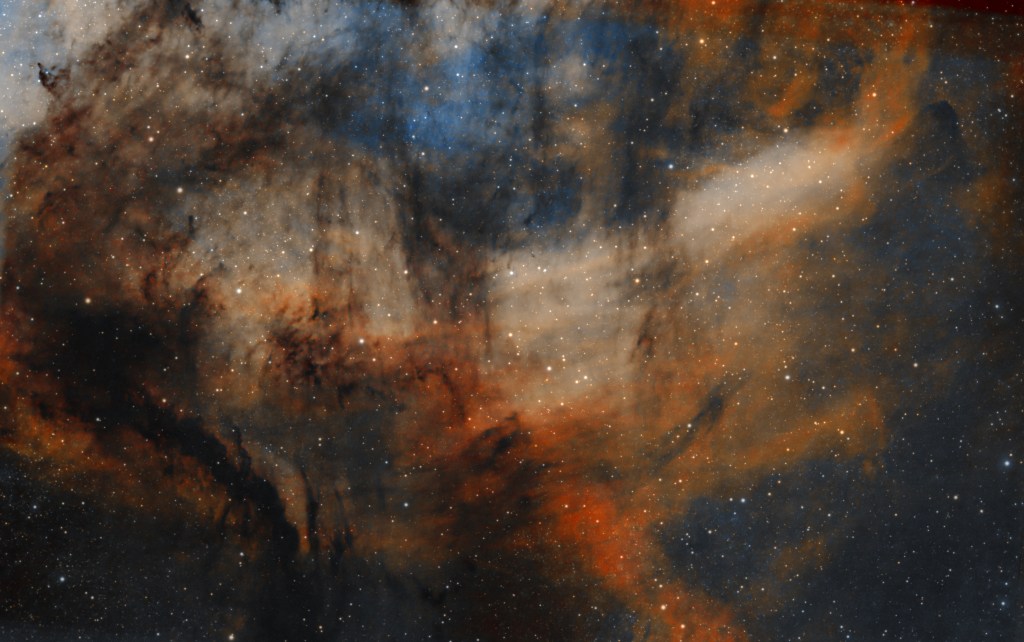
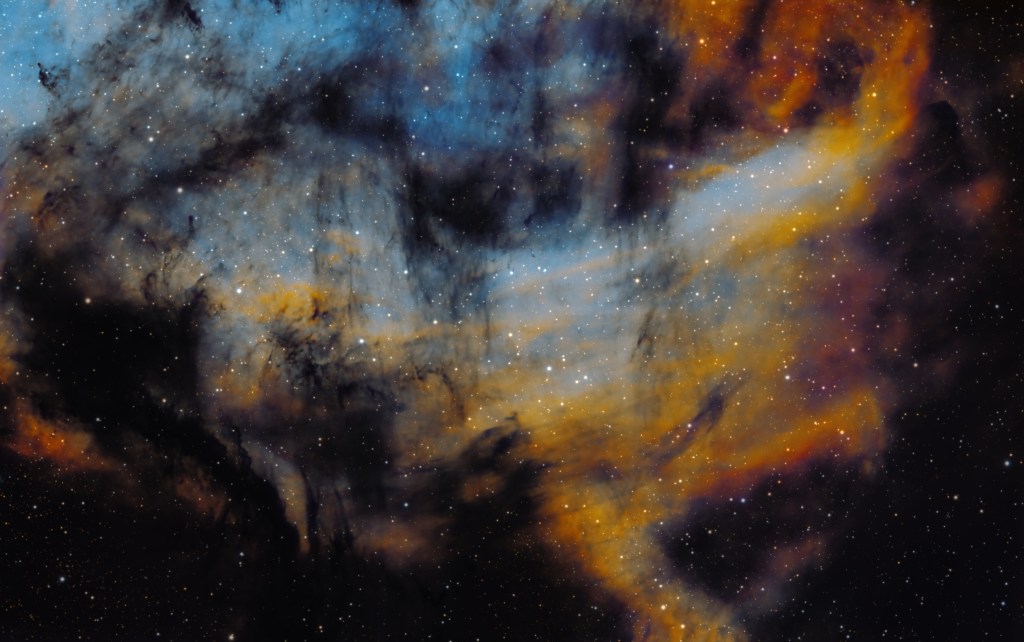
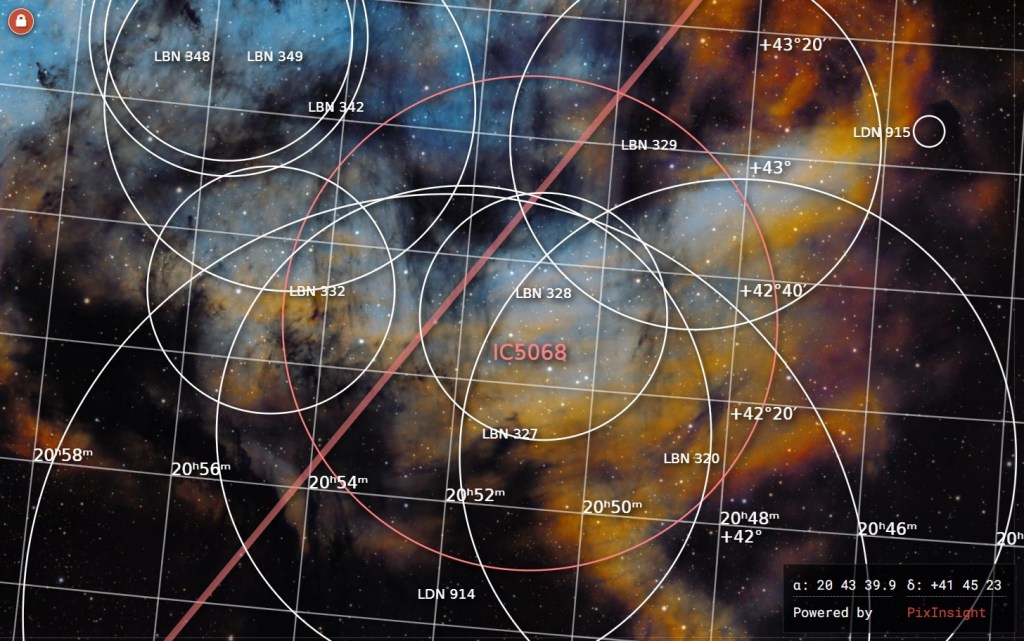
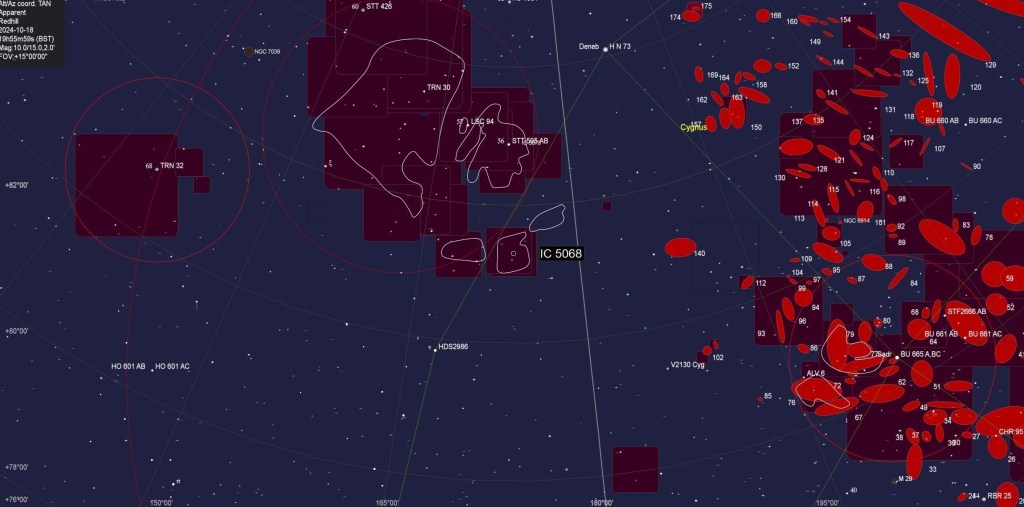
| SEPTEMBER | FORSAKEN NEBULA, IC 5068: This complex area is known for the graphically shaped streaks of cold, dark dust clouds that criss-cross the dense, brightly coloured gas regions of nebulosity. Situated within the adjacent Cygnus molecular cloud just below the Pelican Nebula and close to other more famous objects, this low emission nebula is unfortunately known as the Forsaken Nebula! | |
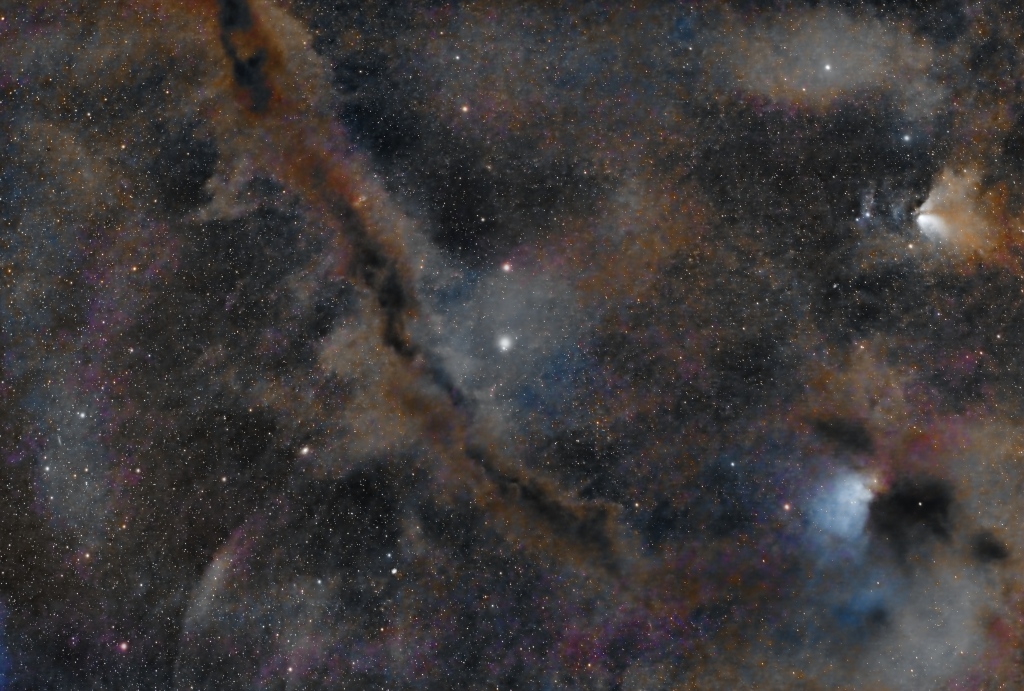
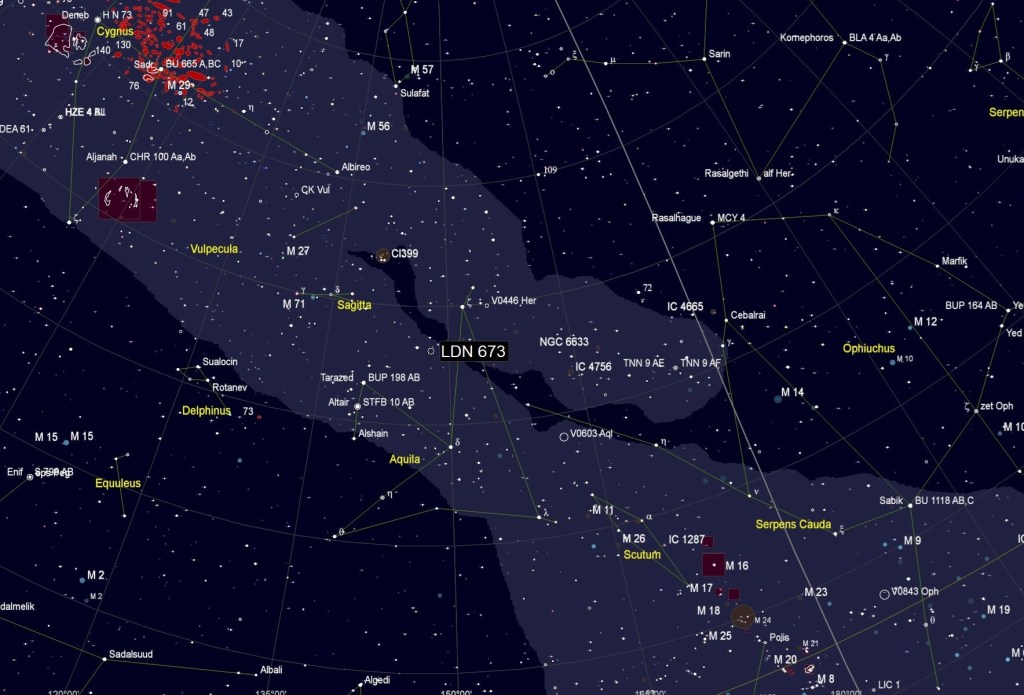
| OCTOBER | THE CHINESE CHARACTER, LDN 673*: It might seem paradoxical but often it is the absence of light that makes an image interesting. About 600 million light-years from Earth, within the Aquila constellation, is Lynd’s Dark Nebula (LDN) 673. Some 7-light years in size, this fragmented dark molecular cloud complex contrasts against the colourful molecular clouds and stars of the Milky Way, which is reminiscent of a Chinese character. | |
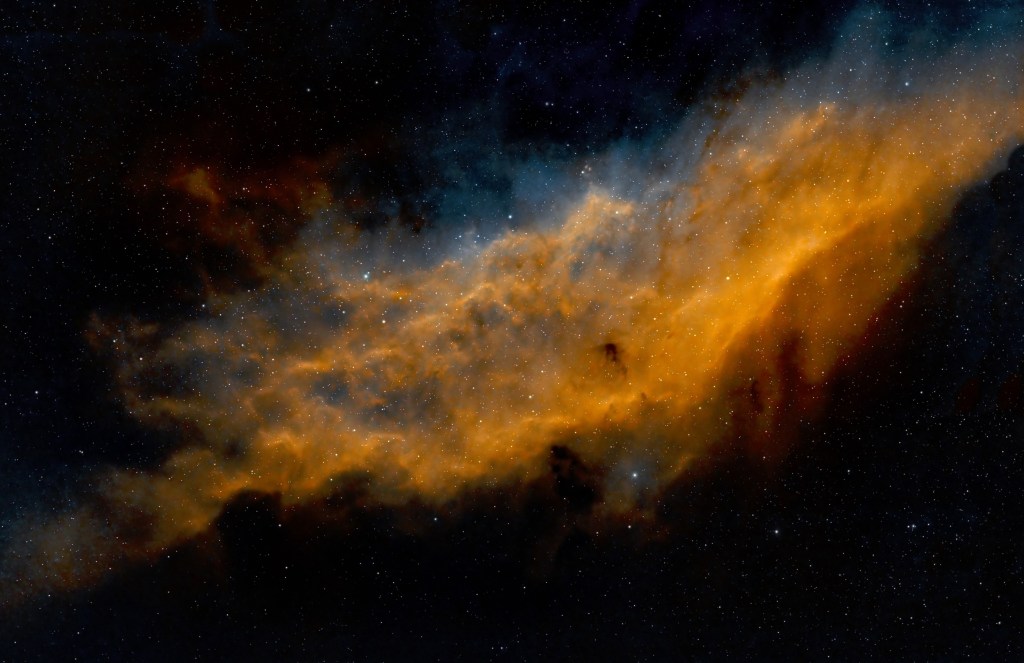
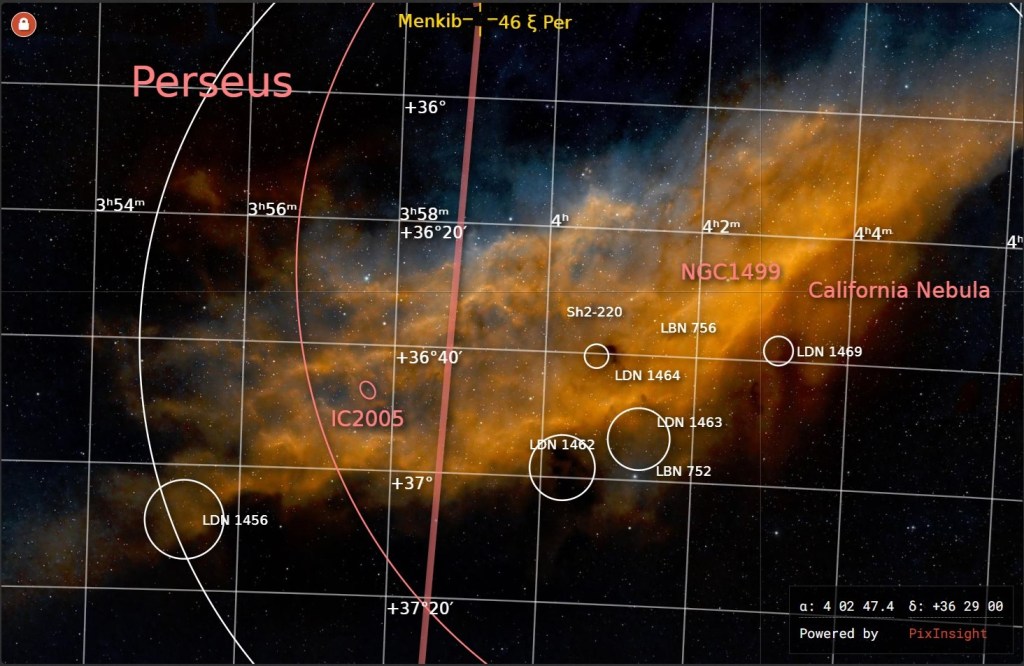
| NOVEMBER | CALIFORNIA NEBULA, NGC 1499: Located in the Perseus constellation, in the Orion arm of the Milky Way 1,000 light-years from Earth, NGC 1499 is a large emission nebula about 100 light-years long. First imaged in 2016, new improved data and processing now discloses the full grandeur of this object. | |
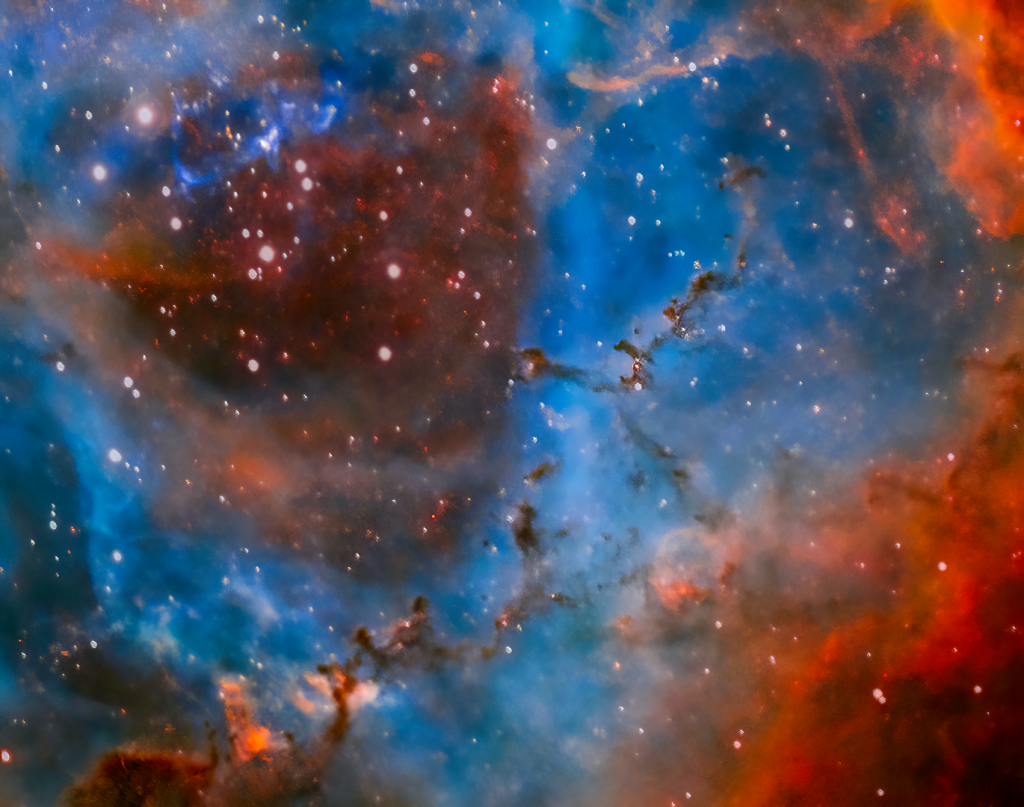
| DECEMBER | ROSETTE NEBULA, NGC 2244: Approximately 5,000 light-years away, the vast cloud of gas and dust had been sculpted into the distinctive rose-like shape, while meanwhile a central star cluster has blown-away a large hollow within the molecular cloud. Revisiting this old favourite for the fourth time since 2015, here I have experimented with an unusual colour palette combination that has produced an exciting alternative image of the night sky’s rose. | |
| Footnote: All images taken from Redhill, Surrey or at a dark sky site in New Mexico, USA shown by an asterisk* | ||
| HAPPY NEW YEAR + CLEAR SKIES FOR 2025 | ||