The year 2025 was like no other. Starting with a knee replacement operation in January, shortly after we finally found a new house in March and moved to the lovely dark skies of Somerset at the end of June. Unfortunately, the ensuing turmoil left only a limited time for astronomy. Notwithstanding, I was able to supplement images from Redhill and our new home in Wookey, with some excellent data from Texas, USA and Chile to produce, what I hope you will agree, is an exciting 2026 calendar.
For other pictures and information, go to my website https://watchthisspaceman.com/ or a video of the calendar can be found here on YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gn3ls_s71lQ and is best accessed on a PC or smart TV screen. Background music this year is Massive Attack’s track Atlas Air.
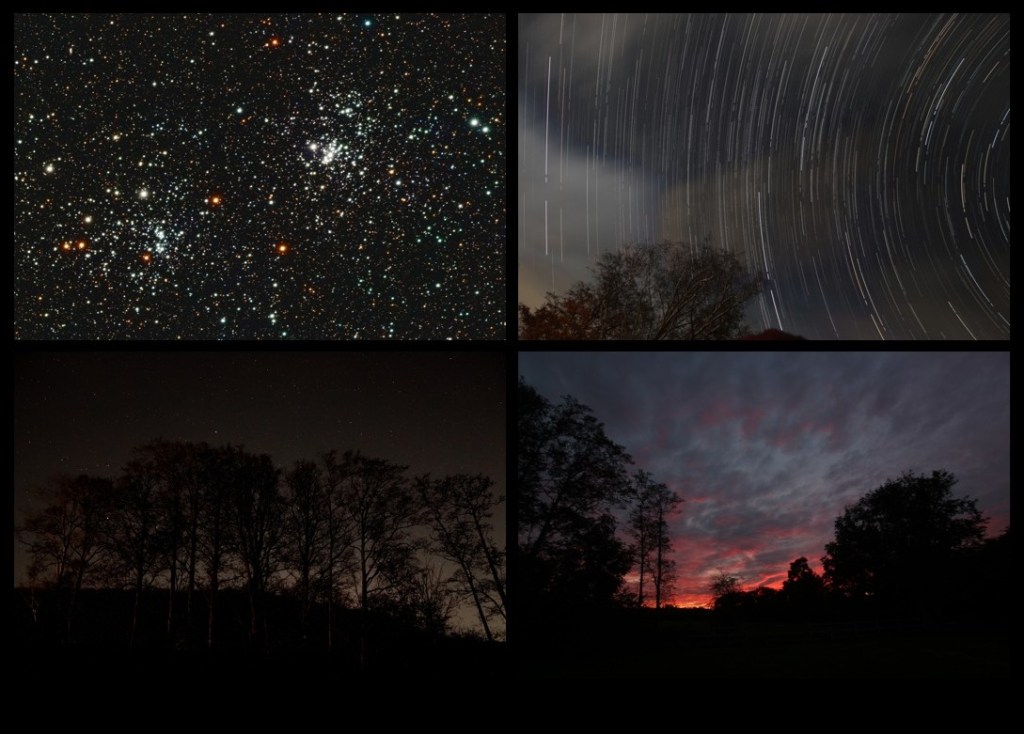
| COVER | NIGHT SKY MONTAGE AT CASTLE FARM OBSERVATORY: All these images (at the top of the page) were taken at various times from the same location at our house in Wookey, Somerset. Clockwise from bottom left: (1) Nightscape of a small coppice looking south (2) Double Cluster – a pair of open star clusters in the Perseus constellation (3) Star trails (4) Sunset looking west. | |
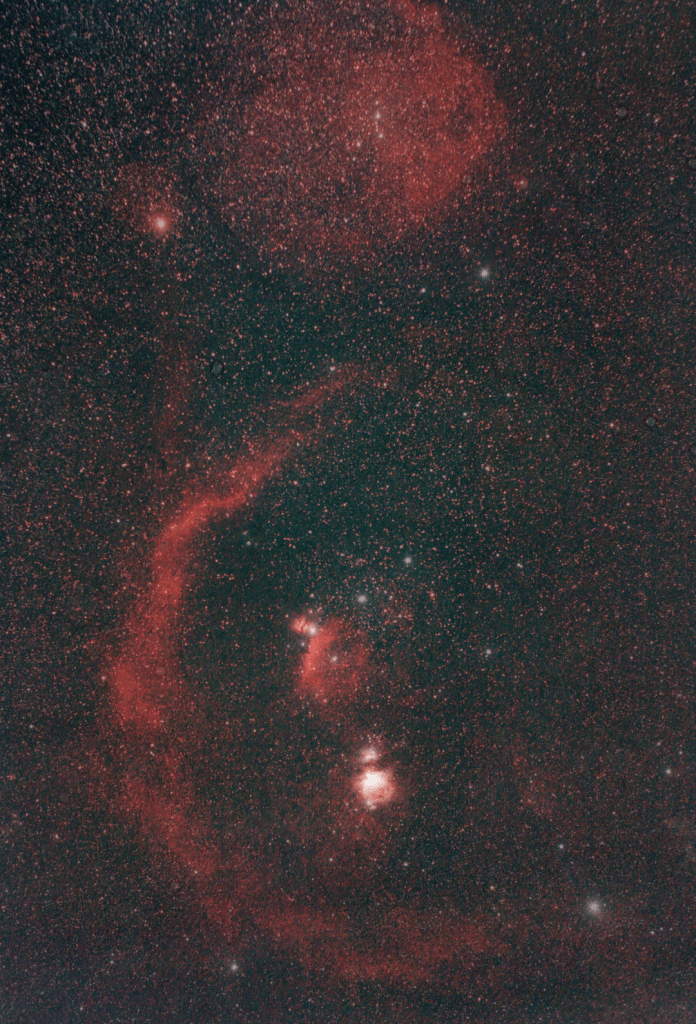
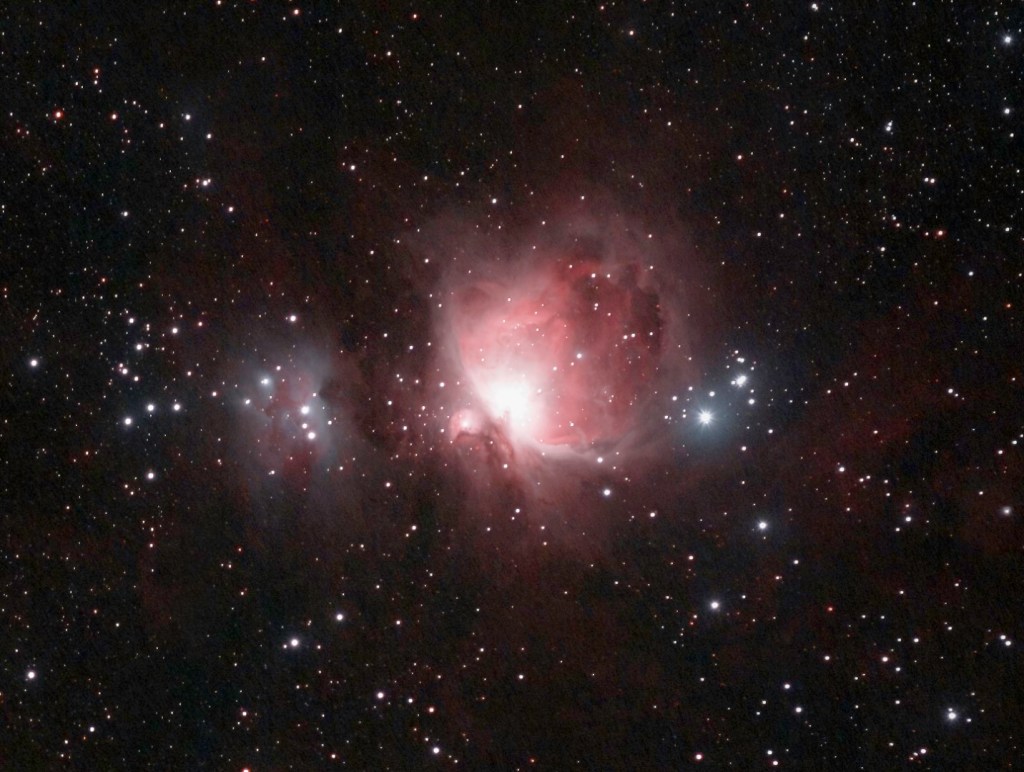
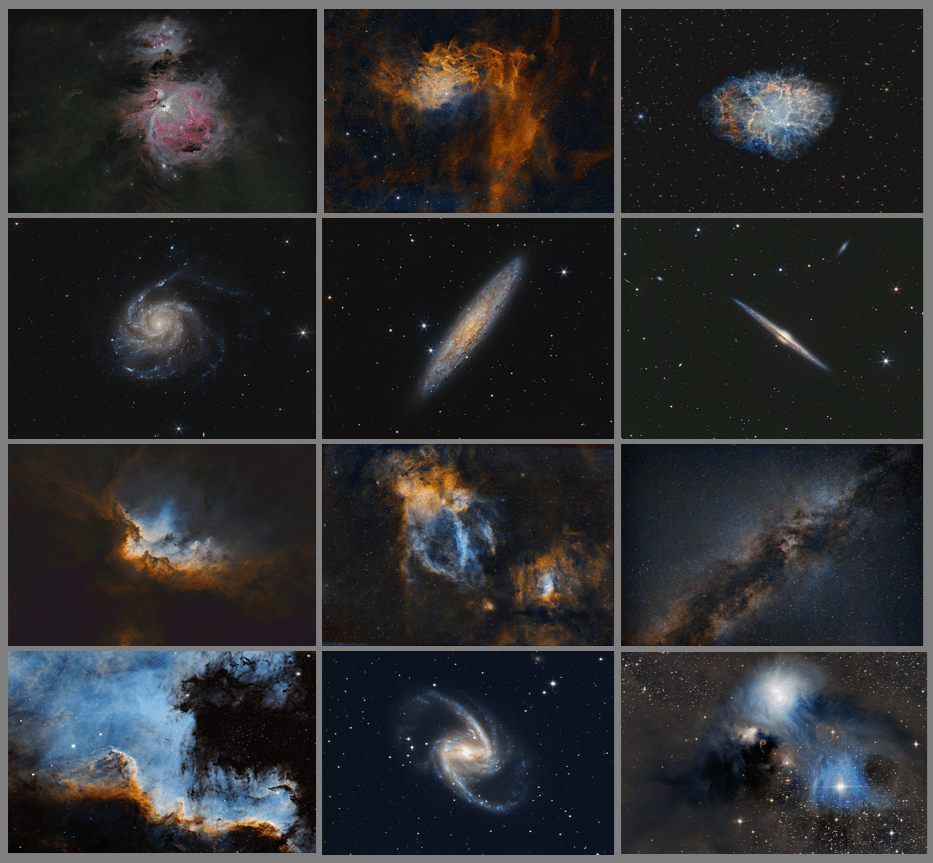
| JANUARY | THE GREAT ORION NEBULA, M42 (1) The Orion Nebula is a gigantic cosmic cloud of interstellar dust and gas, which is the basis for the birth of numerous new stars or a “star nursery”. Being the brightest nebula in the northern hemisphere and just over 1,300 light-years distance from Earth, it can be seen with the naked eye on a clear night. | |
| FEBRUARY | FLAMING STAR NEBULA, IC405 (1) This nebula is illuminated by a powerfully bright blue variable star, AE Aurigae. The object’s epithet comes from the brightly lit ripples of gas and dust at the top of the image, illuminated by AE Aurigae and glowing hydrogen gas. This “runaway star” was ejected by a collision two million years ago from the Triangulum region of The Great Orion Nebula. | |
| MARCH | CRAB NEBULA, M1 (3) This small but beautiful supernova Remnant (SNR) was the result of the explosion of the star CM Tau just over 970 years ago. Located at the centre of the nebula, the remaining Crab Pulsar neutron star spins at the rate of 30 times per second. | |
| APRIL | PINWHEEL GALAXY, M101 (3) At nearly twice the size of the Milky Way and containing at least an estimated trillion stars, M101 is the second largest galaxy of the Messier catalogue and certainly one of the highlights of the spring galaxy season. | |
| MAY | SCULPTOR GALAXY, NGC 253 (3) One of the advantages of obtaining data from Texas, USA, is that it enables views of objects in the Southern Hemisphere that are impossible from the UK. Also known as the Silver Dollar, it is one of the brightest galaxies in the night sky, which results from very high rates of star formation that are fed by the abundance of thick dust lanes. | |
| JUNE | NEEDLE GALAXY, NGC 4546 (3) Seen edge-on from Earth, the Needle Galaxy is thought to be a barred spiral galaxy, some 33% larger than the Milky Way. It has at least two satellite galaxies and 240 globular clusters. Seen through a telescope the Needle Galaxy appears like a thin streak drawn across the dark night sky but look closer and its detailed magnificence is revealed. | |
| JULY | WIZARD NEBULA, NGC 7380 (2) Formed only a few million years ago, the gases of this young emission nebula glow due to intense radiation from hot, massive stars within. Interwoven within this glowing gas are dark, dense regions of dust that sculpt the nebula’s dramatic and somewhat mystical appearance, in this case a wizard – which marks my first image from Somerset. | |
| AUGUST | LOBSTER CLAW & BUBBLE NEBULAE, SH2-157 & NGC 7635 (2) Located in the Perseus Arm of the Milky Way, the Lobster consists of ionized hydrogen gas energized by ultraviolet radiation from nearby hot, young stars. The nebula’s distinctive claw-like shape arises from intricate filaments of glowing gas and dark dust. Nearby the Bubble Nebula owes its distinctive looks to a single, massive star, which emits fierce stellar winds that sweep up the surrounding gas into a nearly perfect, glowing shell. | |
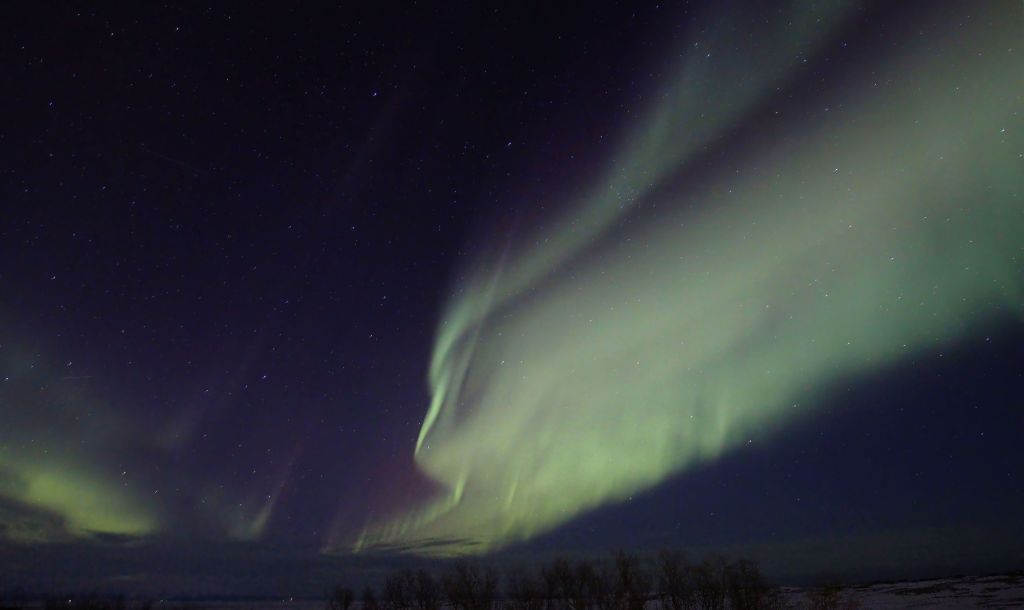
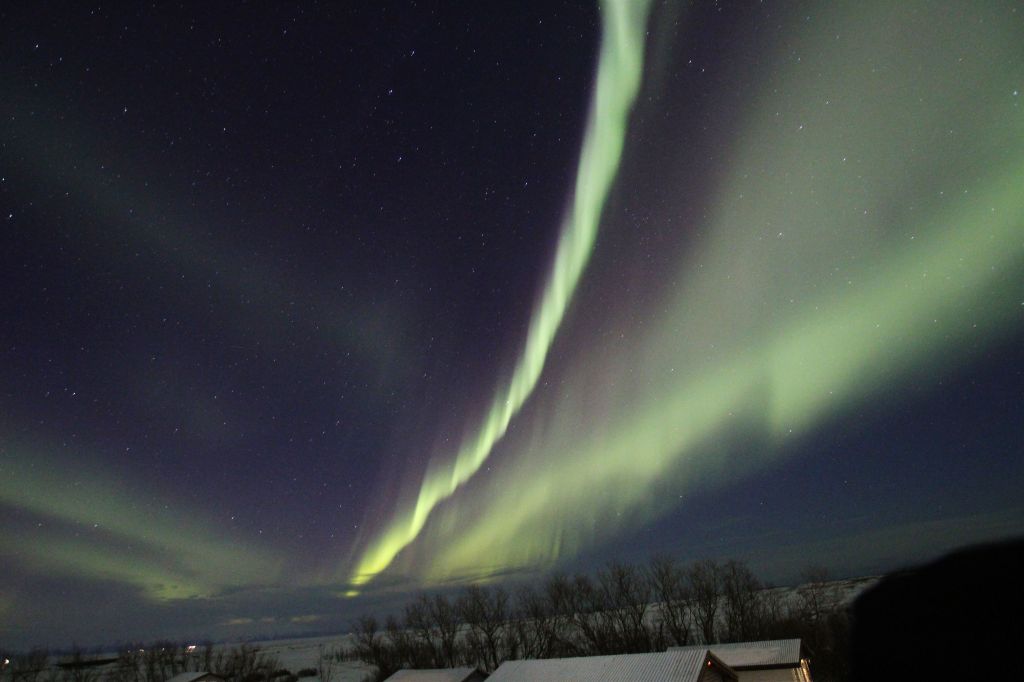
| SEPTEMBER | MILKY WAY (2) The night sky in Somerset is three times darker than Redhill, providing significantly better astronomy views. In this case a spectacular image of the Milky Way’s galactic centre. | |
| OCTOBER | THE CYGNUS WALL (2) The Wall is a prominent ridge located within the much larger North America Nebula in the Cygnus constellation. It is an active star-forming region, about 20 light-years long, composed of gas and dust that glows from the energy of young stars. | |
| NOVEMBER | GREAT BARRED GALAXY, NGC 1365 (4) A double-barred spiral galaxy located 56-million light-years away, spans over 200,000 light-years across, twice the Milky Way. The most distinctive feature is its massive central bar, which plays a crucial role in channelling gas and dust into the galactic core. As a Seyfert galaxy the nucleus is extremely bright due to energetic processes around its black hole. | |
| DECEMBER | CORONA AUSTRALIS, NGC 6729 (4) This spectacular image is a combined reflection and emission nebula, set within the Australis Molecular Cloud. This wonderful, hazy looking nebula unusually exhibits both variable brightness and morphology over time. | |
| Image Data Source: (1)Redhill, Surrey (2)Castle Farm, Somerset (3)USA (4)Chile | ||
| HAPPY NEW YEAR + CLEAR SKIES FOR 2026 | ||