Imaging the Milky Way is a popular objective that has so far eluded me, mainly as I suffer from bad light pollution here at Fairvale Observatory. Embarking on a trip to the Southwestern USA recently where dark skies abound, I therefore had high hopes of at last achieving this goal but alas it was not to be and will have to wait for another day.

The trip of a lifetime
As a geologist I have often visited parts of Nevada, Colorado, Utah and California but never the famous sites of the Grand Canyon, Monument Valley, Glen Canyon (Lake Powell), Bryce Canyon and Zion National Park, which this time formed the trip of a lifetime.
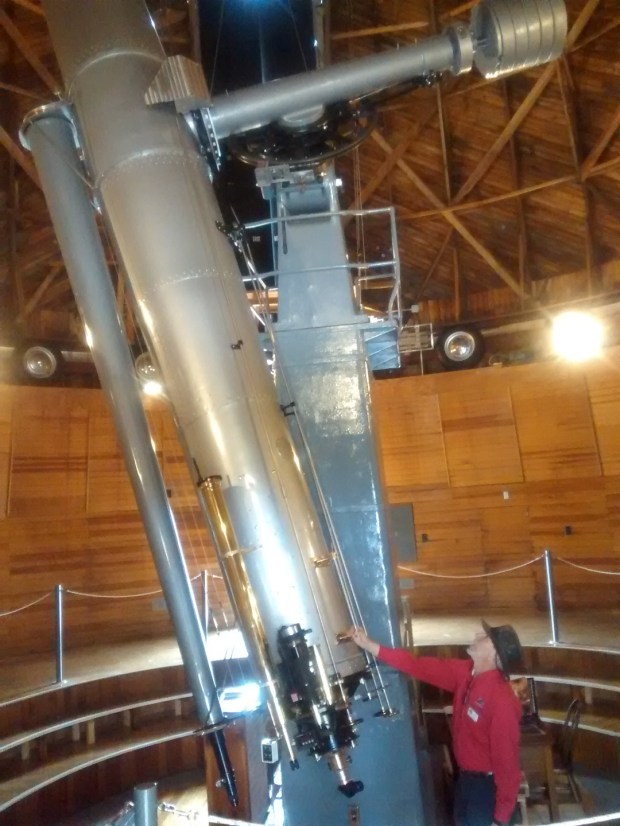

Alvan Clark & Sons 24″ refractor telescope at Lowell Observatory, Flagstaff, Arizona
First stop was after flying into Las Vegas was Flagstaff, home of the Lowell Observatory, where Pluto was first discovered and amongst others houses a magnificent 24-inch Alvan Clark & Sons refractor telescope built in 1895, which I hoped to use for viewing at the observatory’s nightly public sessions. Unfortunately this was not to be as the sky remained resolutely overcast throughout the evening, despite good conditions earlier in the day. Notwithstanding, the observatory is a fascinating place and still remains an important centre of modern astronomy studies; the adjacent town of Flagstaff is also home to the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the Northern Arizona University.

Final notes and paper published by Percival Lowell postulating the existence of a Planet X beyond Neptune, later confirmed by Clyde Tombaugh at Lowell Observatory in 1930 and named Pluto
About 40-miles east of Flagstaff is the site of Meteor Crater, the best preserved meteorite impact crater on Earth. Nearly one mile in diameter and over 500 feet deep, the 50,000 year old crater is very big and very impressive. There’s a lot to like about Flagstaff if you’re into astronomy!
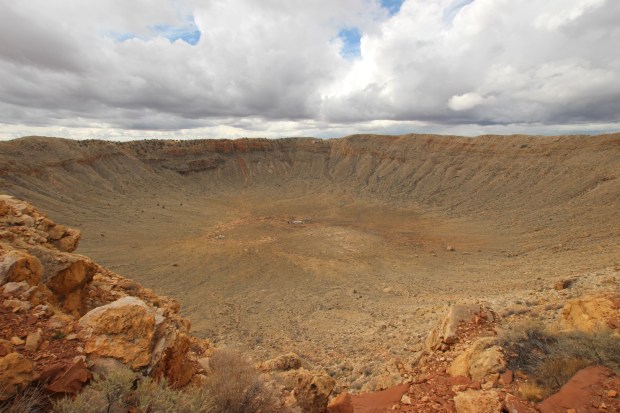

Meteor Crater, Arizona, USA
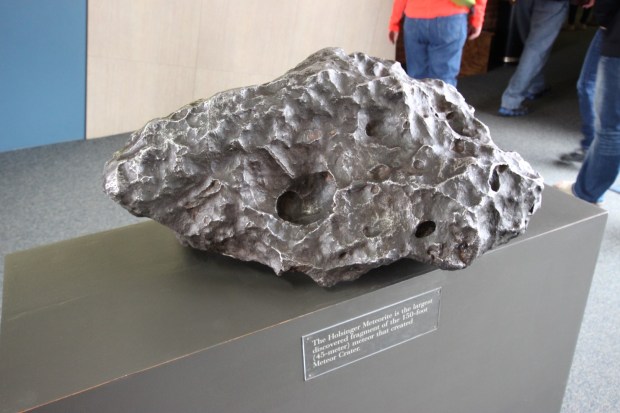

The Holsinger Meteorite: the largest remaining fragment of the 45 metre meteorite that created Meteor Crater
Moving on to the next stop at the Grand Canyon did not disappoint but staying just outside the park the location suffered some light pollution, compounded by cloud during the evening, thus prohibiting any imaging.
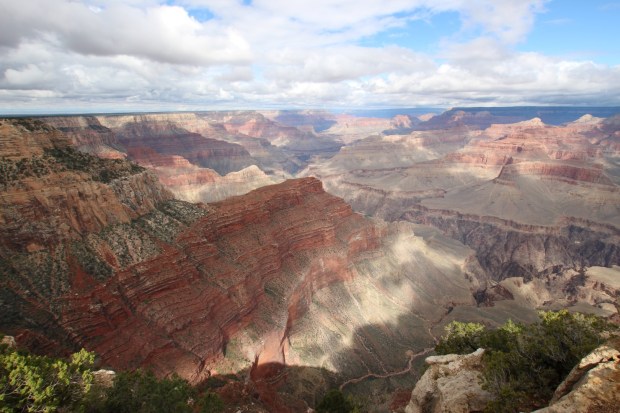

The incomparable Grand Canyon by day. Whilst we stayed around for sunset, unfortunately light pollution and cloud later prevented further nightscape imaging.
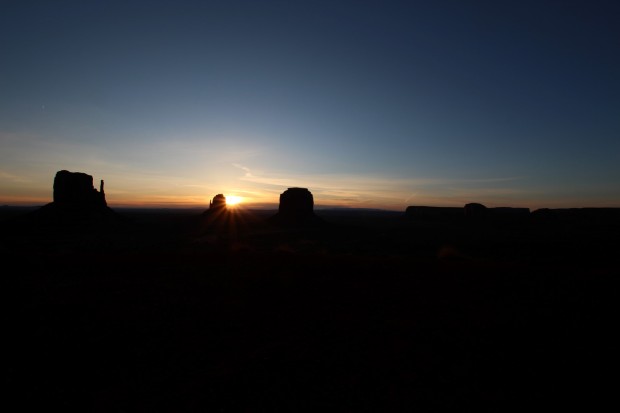
As a more remote location I had always envisaged that next stop at Monument Valley would be my first real opportunity to undertake some night imaging, for which purpose I had taken along the Vixen Polarie and a tripod. In preparation I had previously studied the sky in this part of the world using Cartes du Ciel, which indicated that the Milky Way would be well positioned during my visit; being 35o latitude and 5,000 miles west of Fairvale Observatory meant that the sky was similar to that viewed in the UK three months ago and therefore included my favourite constellation Orion. Unfortunately I had overlooked one problem and my long-time nemesis, the moon.
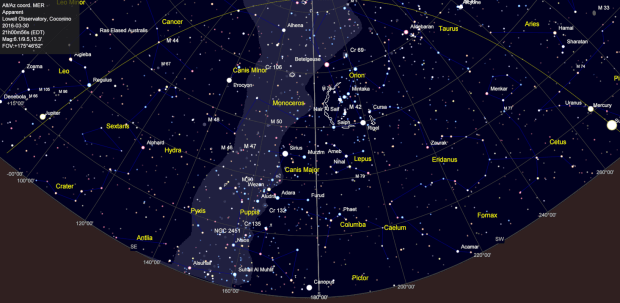
The night sky from Lowell Observatory on 30th March 2016 – no Moon.
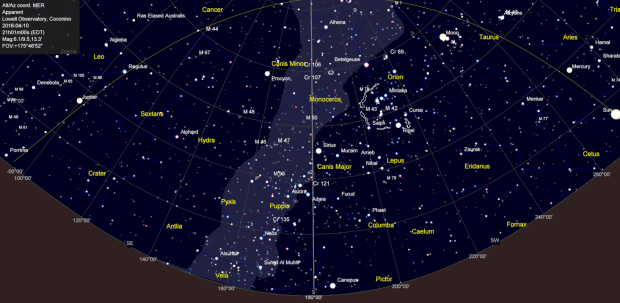
10-days later: night sky from Lowell Observatory on 10th April 2016, now with the Moon!
I was in the USA from 5th to 17th April but for some reason had modelled the sky in Flagstaff on 30th March. It turned out that between then and 10th April, when I was in Monument Valley, the by now half-moon had moved into the night sky and ruled out any chance of seeing or imaging the Milky Way. Of course, even if I had correctly identified the problem beforehand there was nothing I could do about it but it was still frustrating. Notwithstanding, it was a clear sky and not to be defeated turned to Plan-B, which instead took advantage of the moon’s position and in my opinion turned out quite well.

Monument Valley by Day: left to right – West Mitten, East Mitten & Merrick Buttes
Despite the remote location at Monument Valley there was noticeable light pollution from the hotel and ancillary facilities. However, being on the ground floor it was possible to set-up adjacent to the room’s balcony looking east, which was fortunately in the building’s own shadow, thus enabling a sequence of images to be taken of the night sky set against the buttes that typify this region. UnfortunateIy I overlooked setting the Vixen Polarie to half-sidereal tracking speed, which subsequently resulted in a blurred landscape when stacked but the original subs capture the buttes in some detail, themselves illuminated by the moon’s light = result!
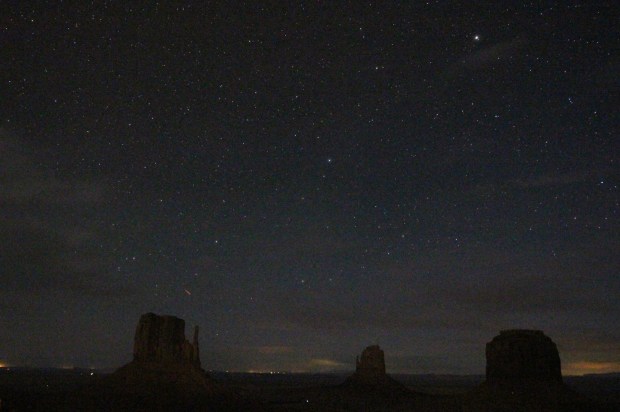

Monument Valley by Night; order of buttes same as above. Canon 700D + Sigma 10mm wide-angle lens | 15secs @ ISO 6,400 | 10th April 2016
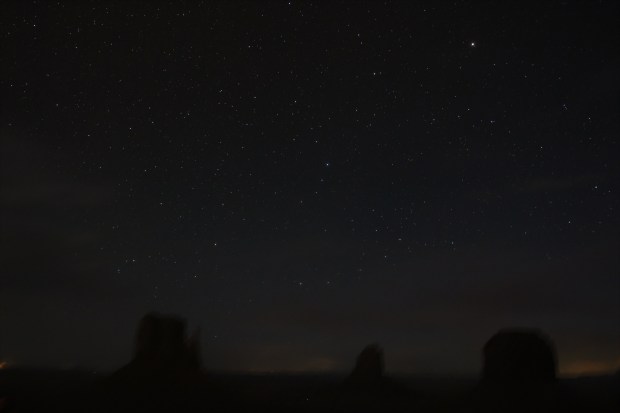

Monument Valley at Night – mulitple stacked shots: Sidereal tracking results in better sky but blurred landscape. Canon 700D & 10mm Sigma wide-angle lens | 20 x 15 secs @ ISO 6,400
Three days later I was in Bryce Canyon, the location of extraordinary geological features called hoodoos, which are the result of unusual and extreme weathering of the limestone cliffs found there. The land forms consist of thousands of various sized pillars of white and red limestone, seemingly lined up like soldiers along miles of the east facing limestone cliff face. Once again I used the moon to illuminate and capture the scene, this time using half-sidereal tracking. The result is somewhat haunting in nature but shows almost as much detail into the far distance as during daytime; I still find it incredible how sensitive the camera’s sensor is in gathering available light at night when extending exposure times and / or turning up the ISO setting.
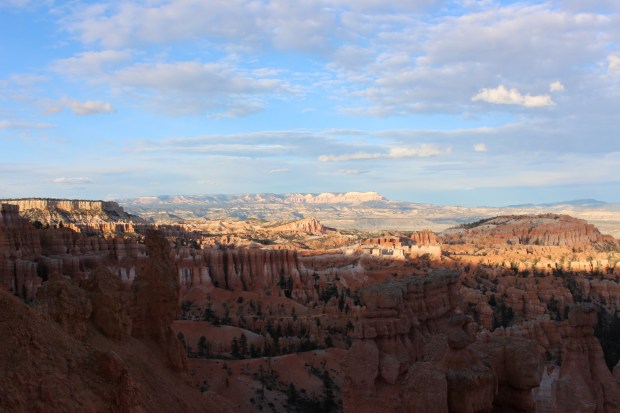

Bryce Canyon at Sunset Point by Day
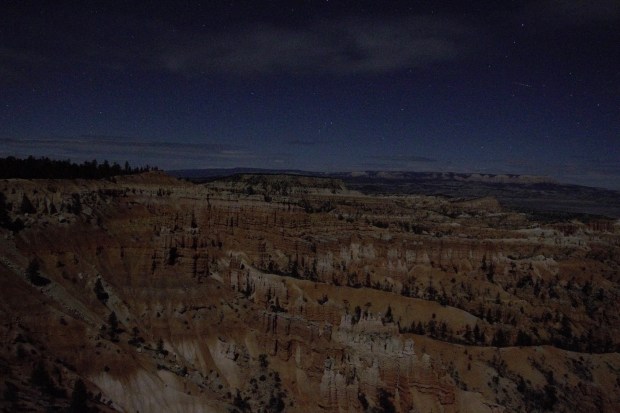

Bryce Canyon at Sunset Point by Night: Canon 700D + Sigma 10mm Wide-angle lens | 15 secs @ ISO 3,200 | 13th April 2016
It is clear I have much to learn about the deceptively simple nightscape photography using the Vixen Polarie but it is equally clear that the equipment provides significant potential and I look forwards to catching the Milky Way one day when the sky is clear and the moon absent. Notwithstanding the disappointment of missing out on the Milky Way this time, in the spectacular big country of Southwestern USA the sky’s the limit and I hope to go back again one day.
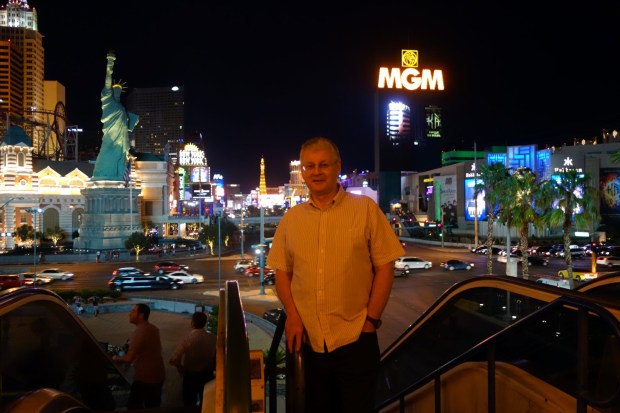

Too much light pollution perhaps? Even in the Big Country of the Southwestern USA getting the right conditions for astrophotography remains a gamble!