It’s early days at my new Castle Farm Observatory and I’m still feeling my way into the benefits of Somerset’s superior darkness, which is noticeably better than my previous home in Surrey. But my new Bortle 4 location is not without some issues: there are a couple of nearby streetlights that can now find its way to my observatory since autumn leaves have fallen, occasional vehicle lights pass by and, inevitably, sections of the sky are obscured by our house and trees.
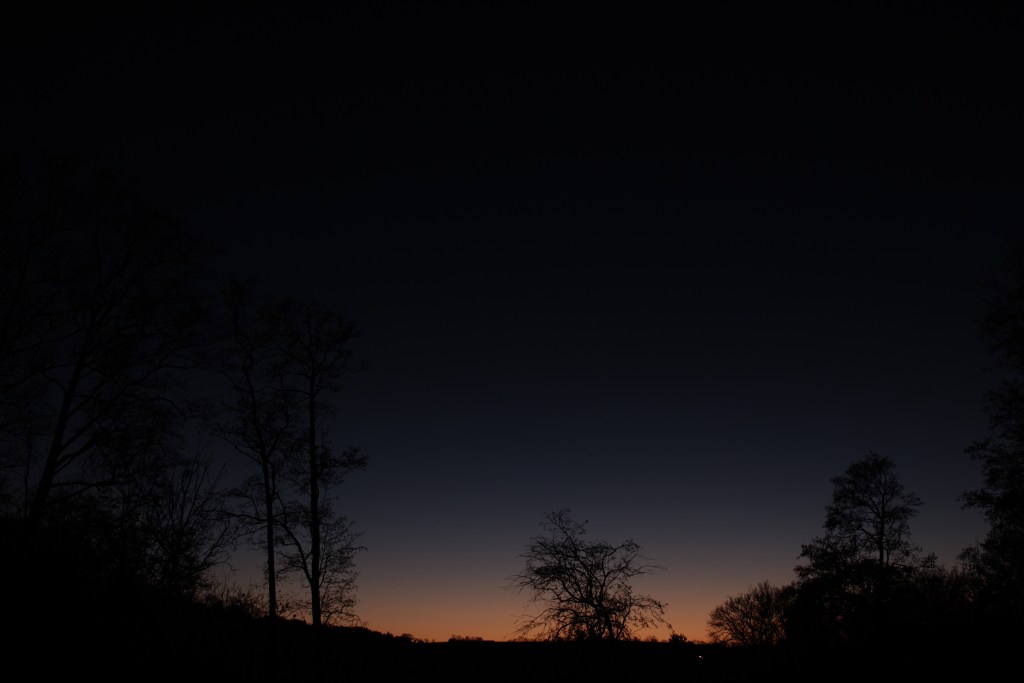


South view, with my house just out of shot on the left!
After more than 12-years of imaging almost exclusively looking south, I must now adjust imaging plans looking southwest or north, which are my main sightlines in Somerset. This might seem a minor issue but as the sky moves around an axis defined in the north by the Polaris star, it thus follows an inclined equatorial grid relative to Earth and the impact on potential imaging plans can be quite profound. Previously looking southwards, the transit of objects during the night (and day) was from the east to west horizons, which on a clear night enabled up to 6-hours imaging of a single object, compared with a westerly view which only catches the latter period of the aforesaid transit. As a result, objects I used to image say from November onwards now only appear in the available (western) section of sky two or three months later. On a more positive note, I am now able to image circumpolar objects looking high and northwards for the first time, which has literally opened new world of possibilities.
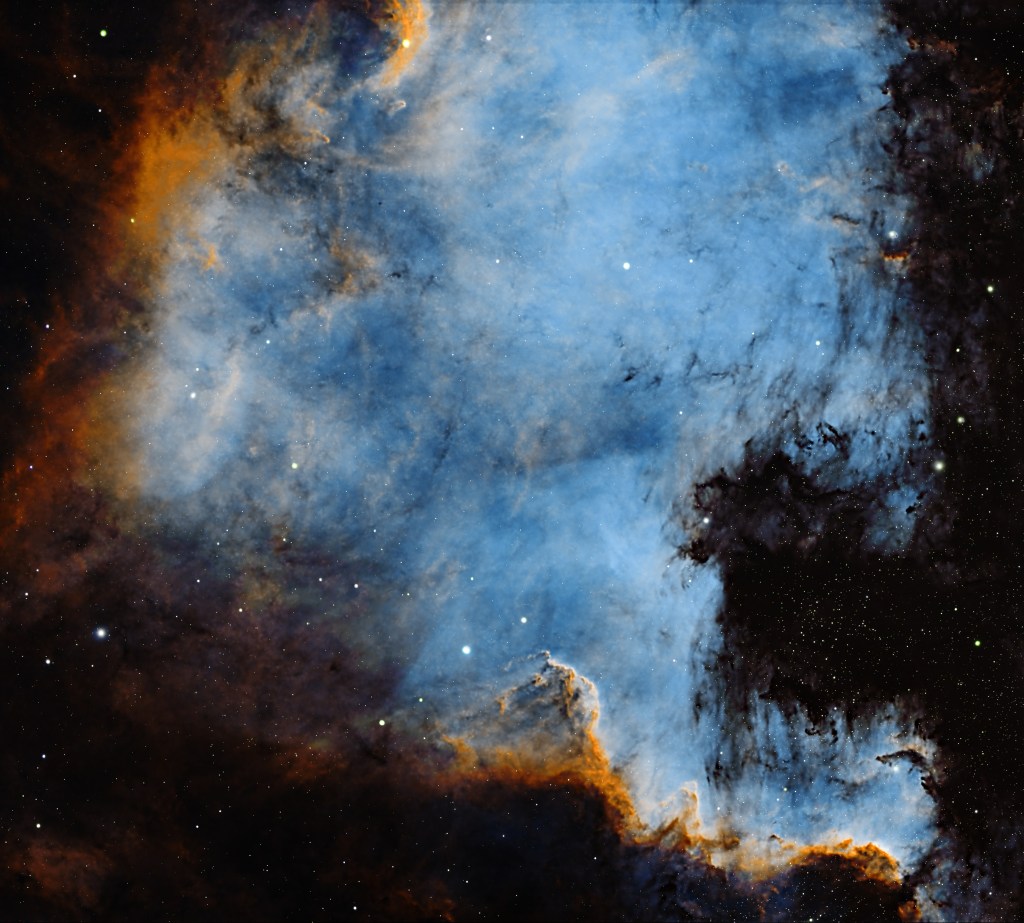
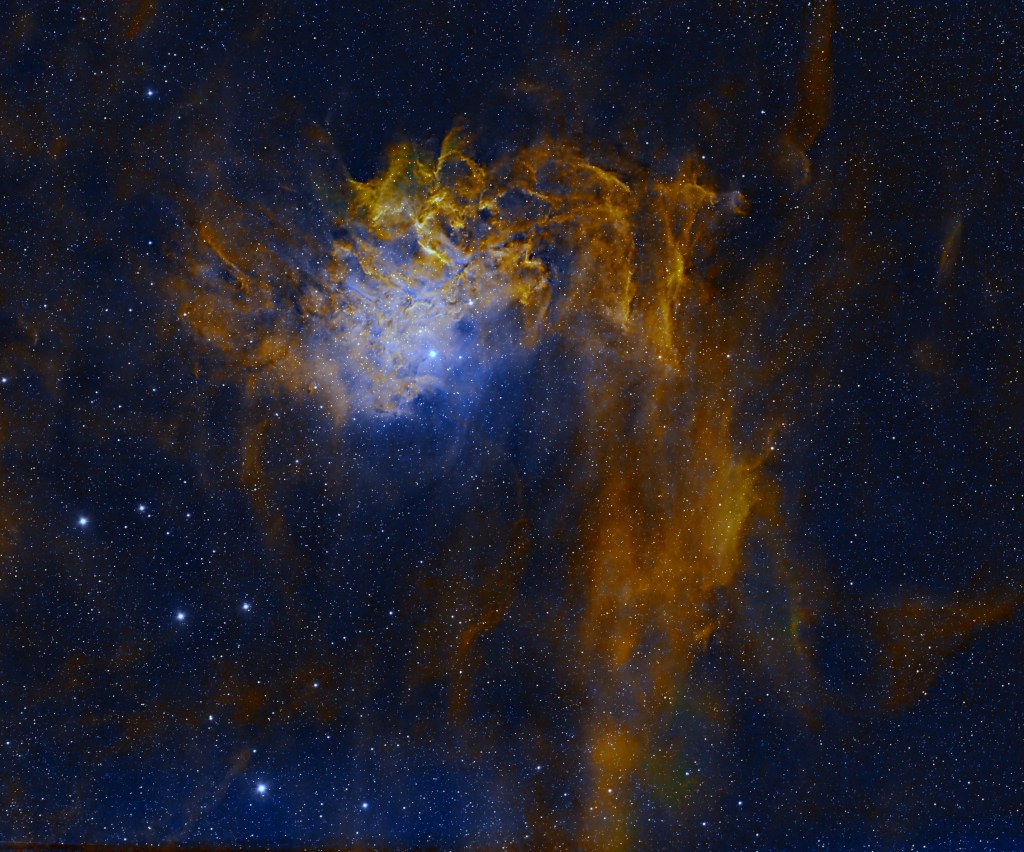
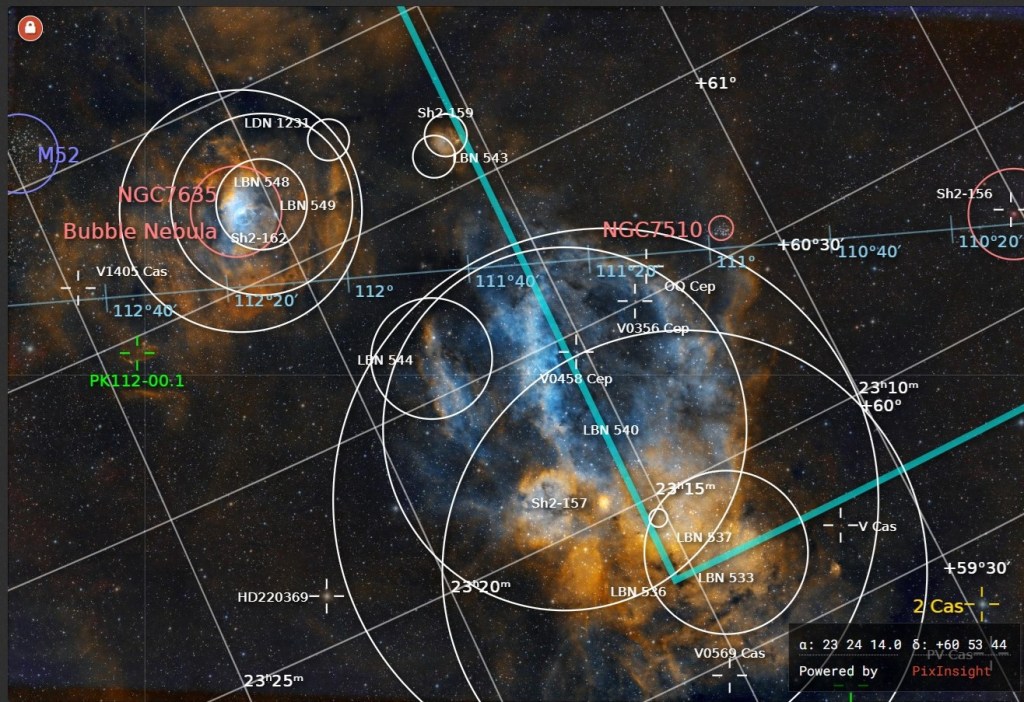
Given the aforesaid issues, I recently chose to image an old favourite which is currently in a favourable position at this time of the year, the North America Nebula (NAN), located high in the early evening night sky looking due west. Spanning some 100 light-years, NAN is a great narrowband object, which by using the Hubble SHO palette always results in an exciting and colourful image.
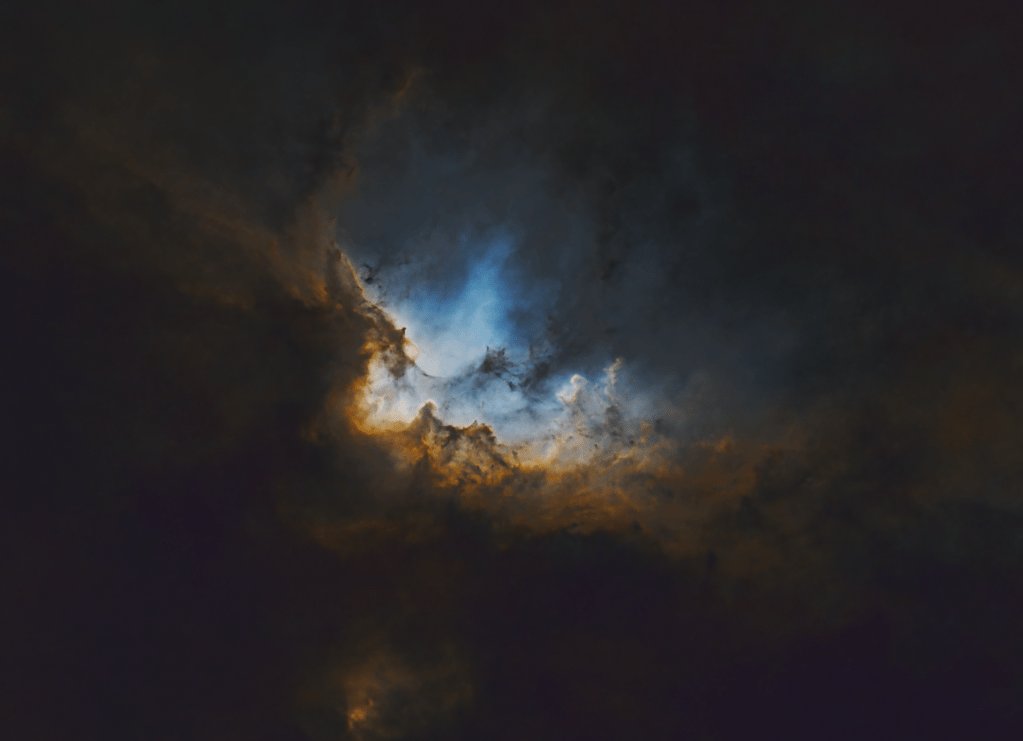
Over two nights I manged to obtain nearly 9-hours of good data, which at my previous Bortle 6 Surrey observatory would probably be the equivalent of more than 12 hours. The final processed SHO image brings all three channels into a delicate balance: vibrant without being garish, detailed without overwhelming noise. The iconic “Gulf of Mexico” region forms a deep void in the nebula, which becomes even more pronounced with the various gradients of blue converging around its dark centre. But on this occasion, I was particularly keen to emphasize details of the fabulous Cygnus Wall (see cropped image below), situated in the lower right corner of the main image i.e. ‘West Texas and Mexico’!
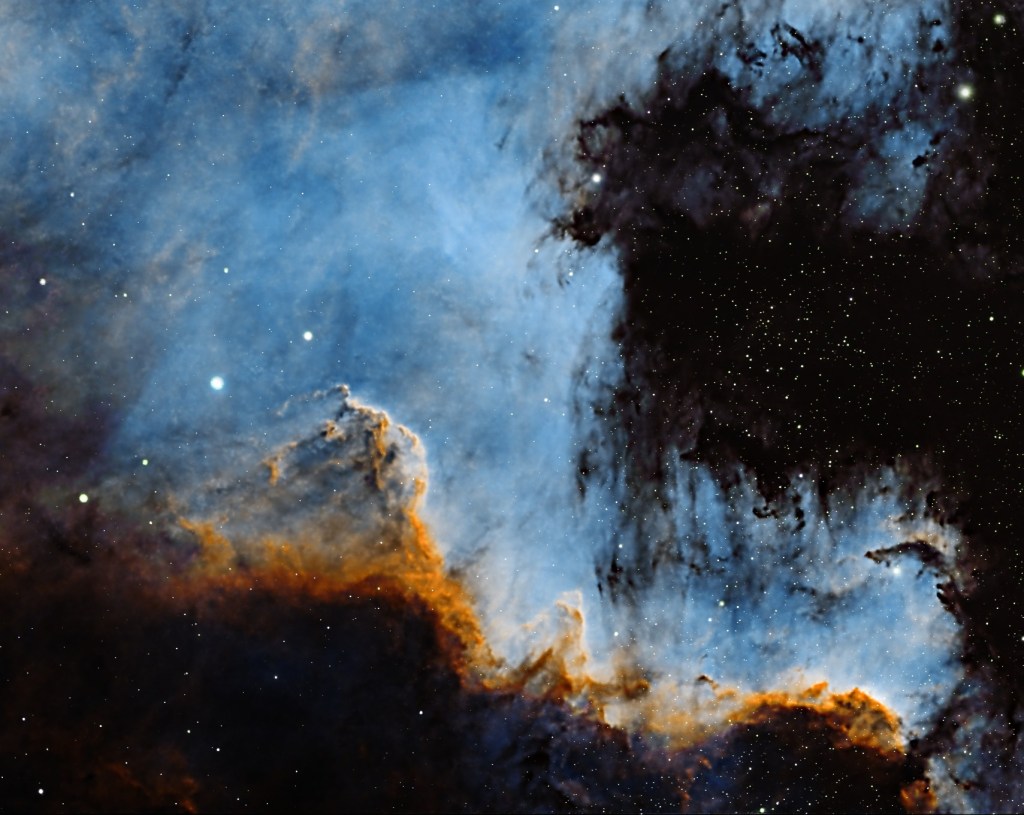

The Cygnus Wall is a striking, heavily sculpted region within the North America Nebula, which itself is worthy of image, which would require a larger telescope. The dense ridge of gas and dust glows brightly as nearby young, massive stars bombard it with intense ultraviolet radiation, causing it to ionize and shine. Its dramatic pillars, ridges, and cavities resemble a cosmic coastline, shaped by stellar winds and ongoing star formation. For some reason it’s been 8-years since I last imaged NAN, except with my Samyang widefield rig, but with the excellent night skies of Somerset I feel sure I’ll be back sooner next time, perhaps with a bigger telescope?
| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | North America Nebula – NGC 7000 |
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Distance | 1,600 light-years |
| Size | Approx. 50 light-years or 2o |
| Apparent Magnitude | +4.0 |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount | SW AZ-EQ6 GT + EQASCOM computer control |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| + Starlight Xpress Lodestar X2 guide camera & PHD2 control | |
| Camera | ZWO1600MM-Cool (mono) CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.65o x 2.0o Resolution 2.05”/pix Max. image size 4,656 x 3,520 pix | |
| EFW | ZWOx8 + ZWO LRGB & Ha OIII SII 7nm filters |
| Capture & Processing | ASIair, Photoshop |
| Exposures | 35 x Ha, 34 x OIII & 36 x SII @ 300 secs (Total time: 8hr 45min) |
| @ 300 Gain 10 Offset @ -20oC | |
| Calibration | 5 x 180 sec Darks 10 x 1/4000 sec 10 x Flats & Dark Flats Ha, OIII & SII |
| Location & Darkness | Castle Farm Observatory, Wookey, Somerset Typically Bortle 4 |
| Date & Time | 19th & 20th November 2025 @ 18.20h |