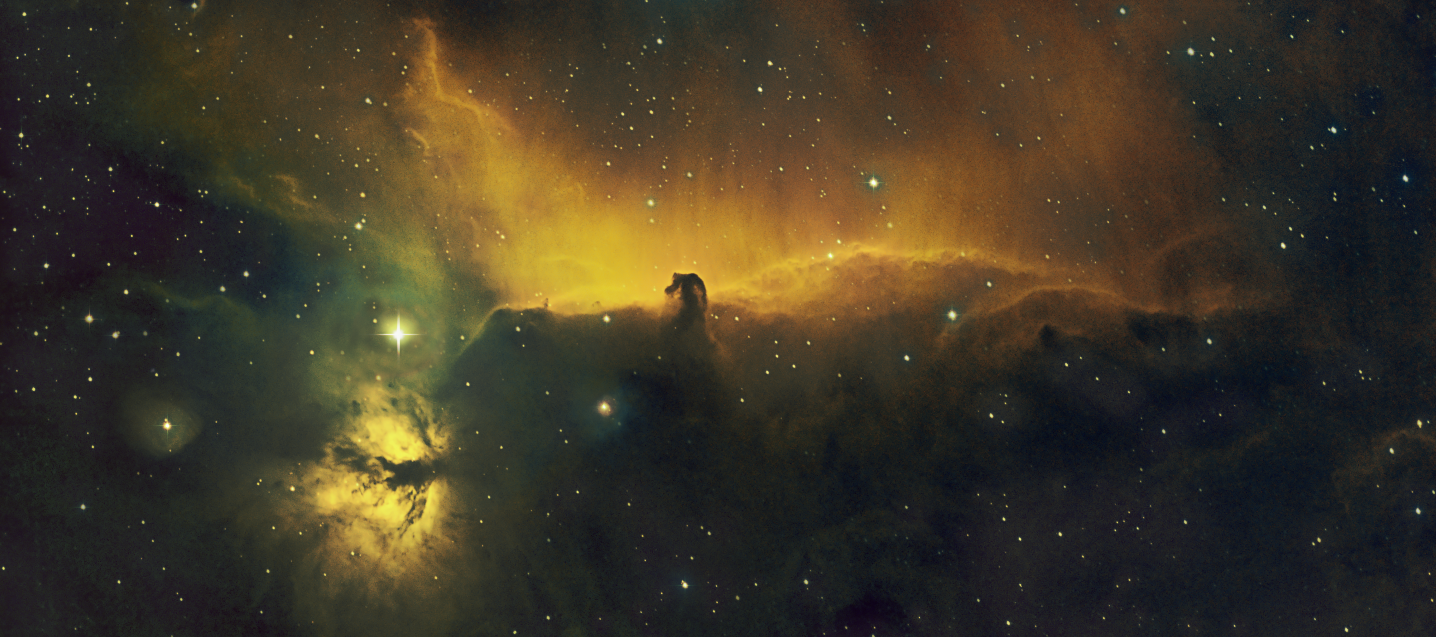
At this time of the year various objects within the Orion Constellation are perhaps the most popular astrophotography targets. Notwithstanding, a few days after imaging The Great Orion Nebula myself early in the New Year, I slewed my camera some 65o further north to the Auriga constellation, location of many other fascinating objects, some of which two years ago I captured in a two panel widefield mosaic. This time it was time to concentrate on just one of those objects, the exciting IC405 AKA the Flaming Star Nebula.
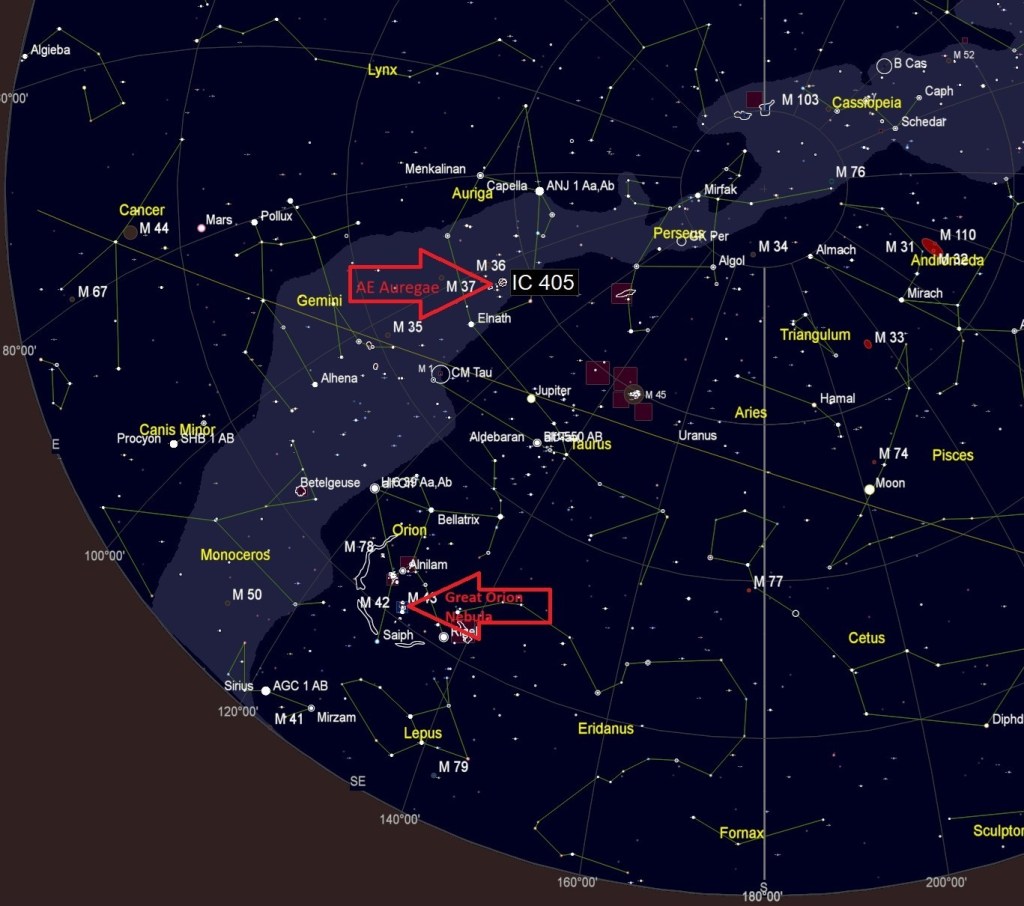
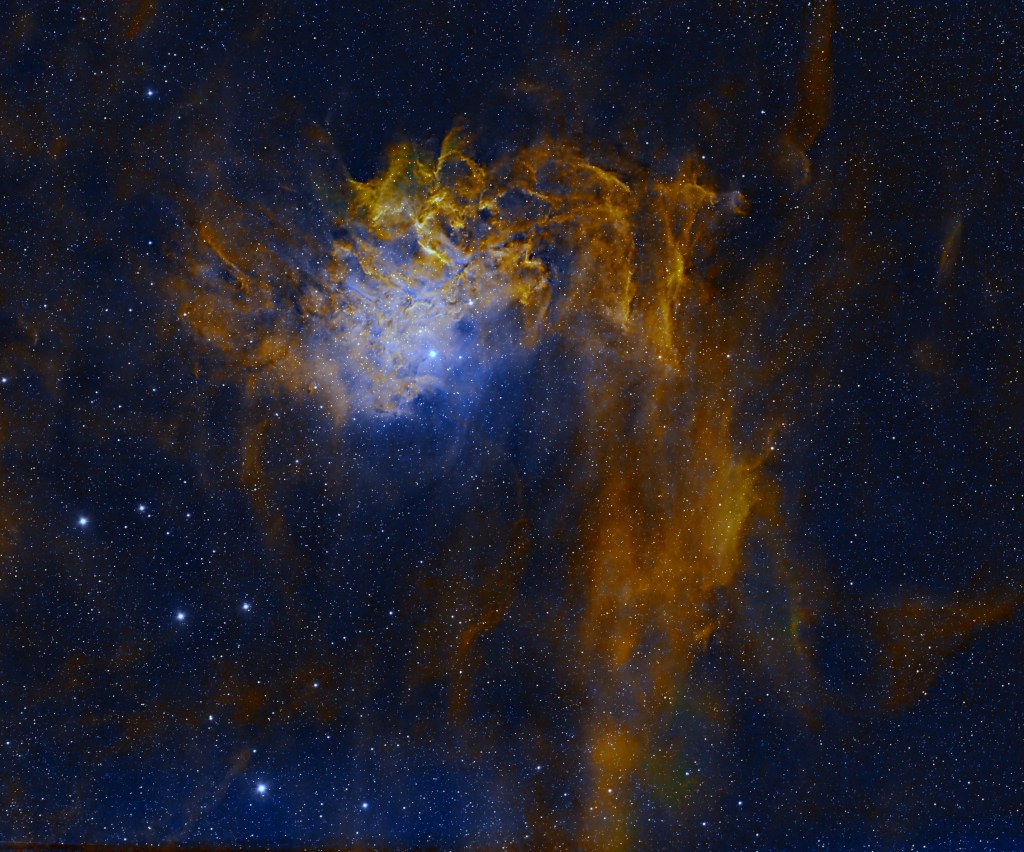
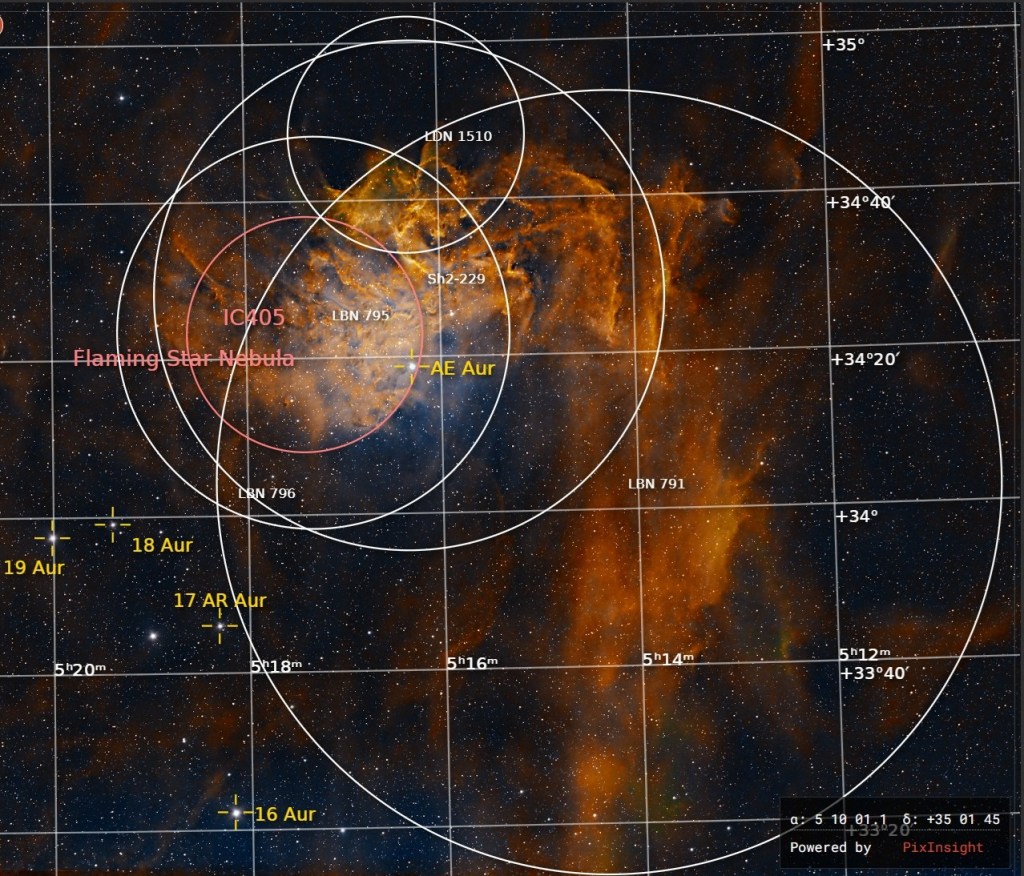
This emission and reflection nebula is a glowing cloud of gas and dust that is illuminated by a powerfully bright blue variable star, AE Aurigae. The object’s epithet arises from the brightly lit ripples of gas and dust at the top of the image, illuminated by the aforesaid AE Aurigae and glowing hydrogen emission. By reducing the dominant reddish hydrogen glow in the image, the full impact bright blue light from AE Aurega can be better appreciated (see image below).

Though some considerable distance from Orion, studies now indicate that the star AE Auriga was probably itself ejected after a collision two million years ago from the Triangulum region of The Great Orion Nebula and, as a runaway star has now made its way to Auriga – what a small world!
| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | IC405 Flaming Star Nebula – Emission / Reflective Nebula |
| Constellation | Auriga |
| Distance | 1,500 light-years |
| Size | 37 x 10 arc min |
| Apparent Magnitude | +6.0 |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount | ZWO AM5 + ASIair plus |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| ZWO120MM mini | |
| Camera | ZWO ASI294MM CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.87o x 1.96o Resolution 2.50”/pix Max. image size 4,144 x 2,822 pix | |
| EFW | ZWOx8 EFW & 31mm Chroma 3nm Ha, OIII, SII & LRGB filters |
| Capture & Processing | ASIair plus, Deep Sky Stacker & PixInsight v1.9.2 |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre = RA 05:15:28.63 DEC +34:09:07.0 Top = North |
| Exposures | Ha x20 + OIII x20 + SII x20 @ 300 sec L x10 + R + G x10 + B x20s @ 60 sec Total Integration Time: 5hr 40 min |
| @ Gain 120 @ -15oC | |
| Calibration | 5 x 300 sec Darks + 10 x NB Flats & Dark Flats LRGB x20 each Flats & Dark Flats @ ADU 32,000 |
| Location & Darkness | Fairvale Observatory – Redhill – Surrey – UK Typically Bortle 5 to 6 |
| Date & Time | 7 & 8 th January 2025 +18.45h |
| Weather | Approx. <=0oC RH >=65% 🌙 50% Waxing |