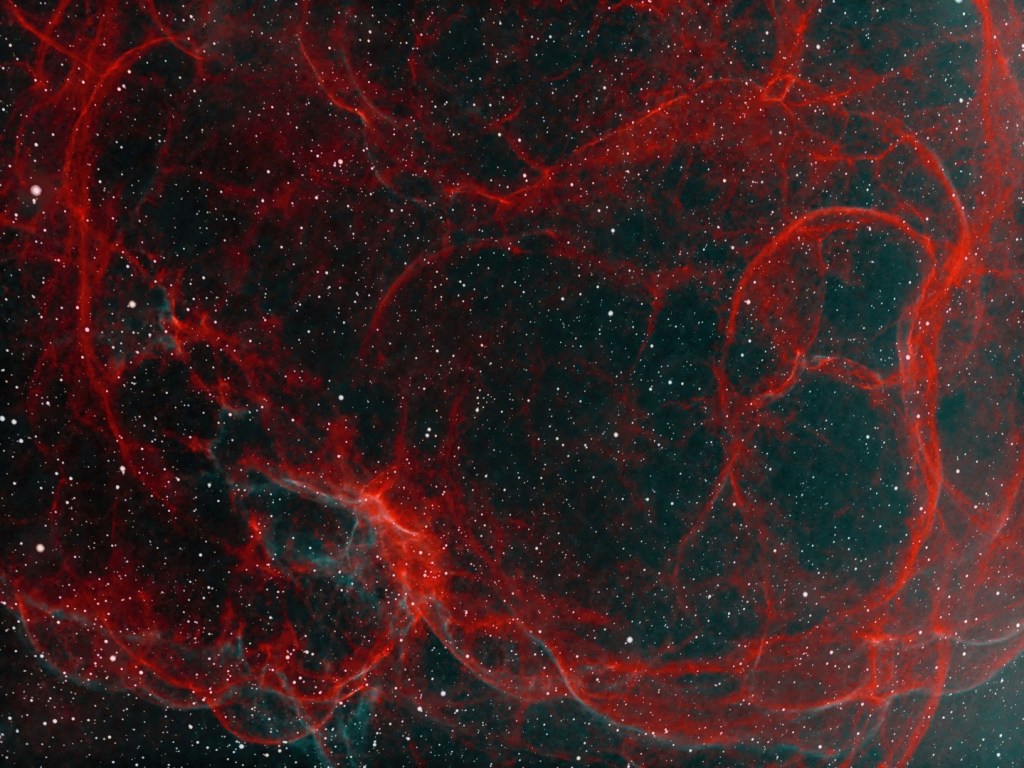
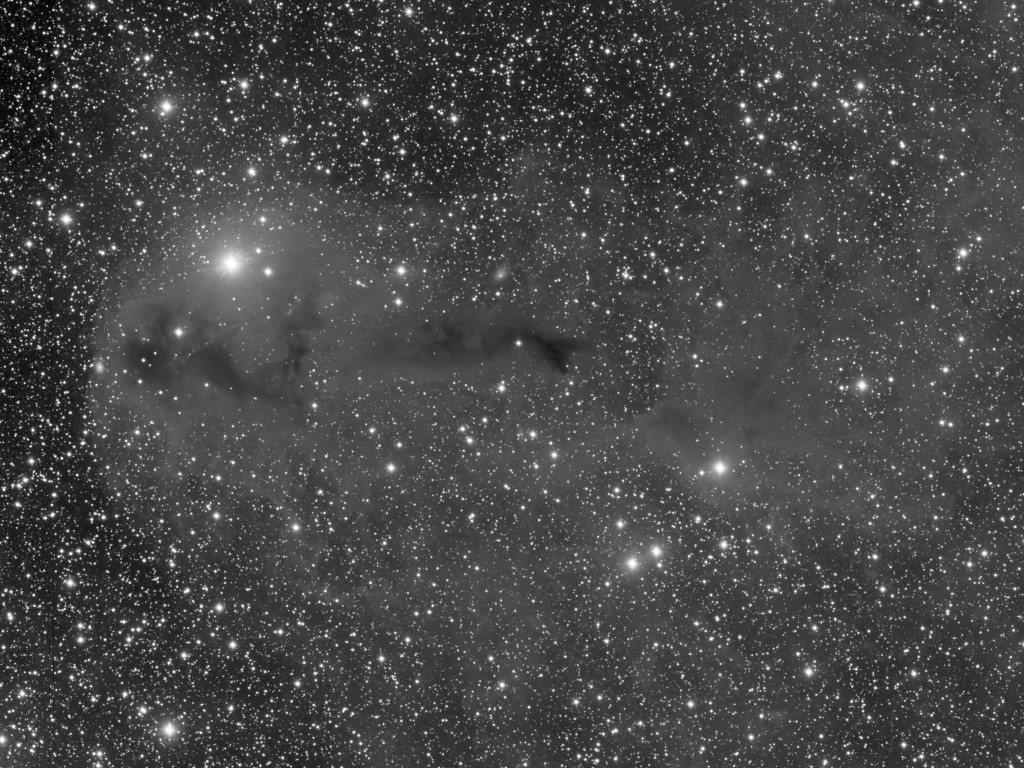
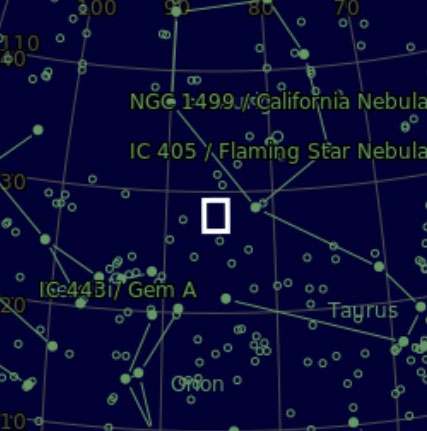
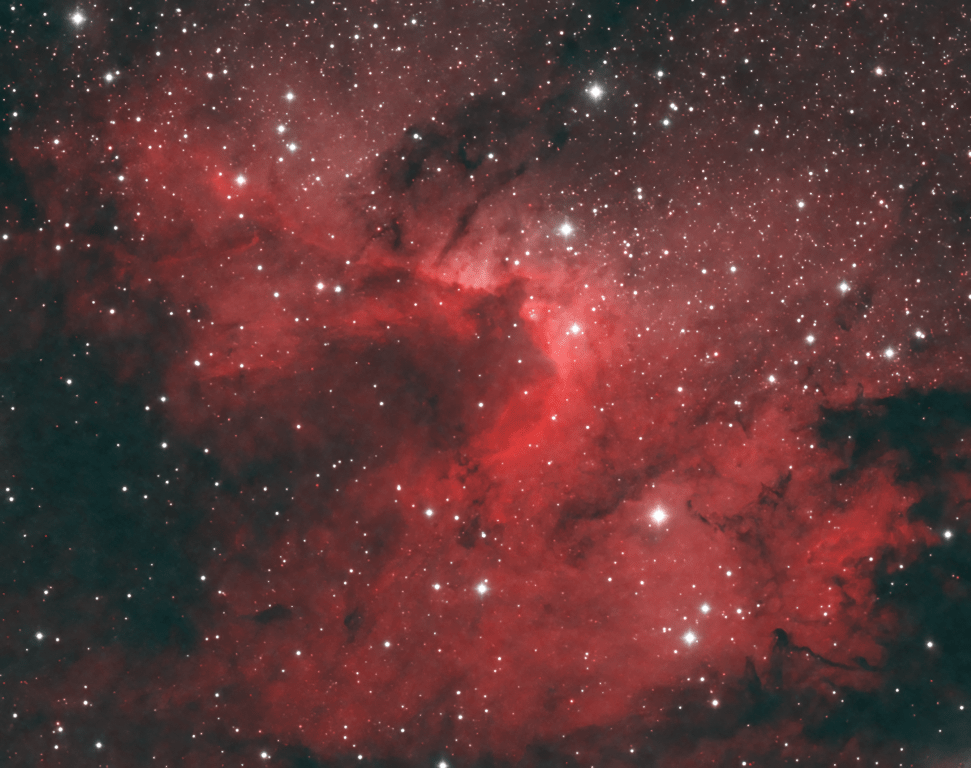
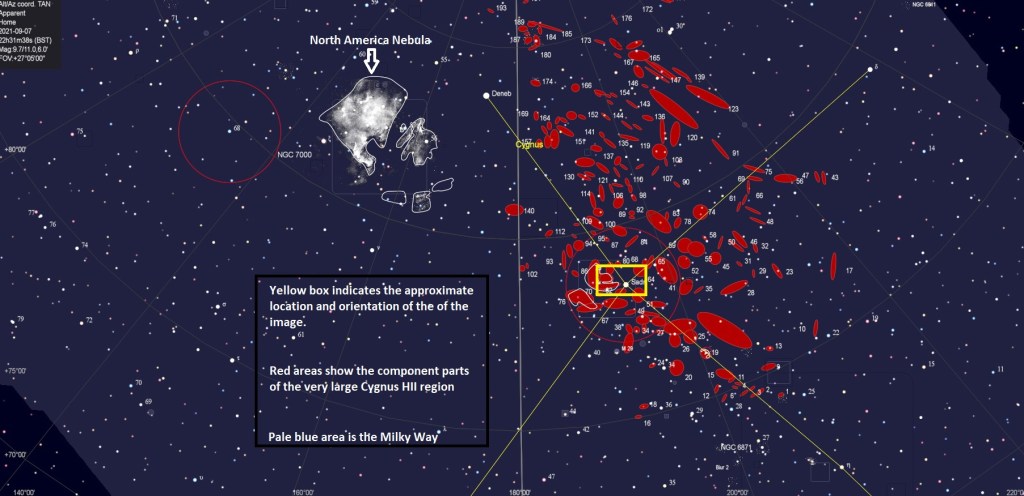
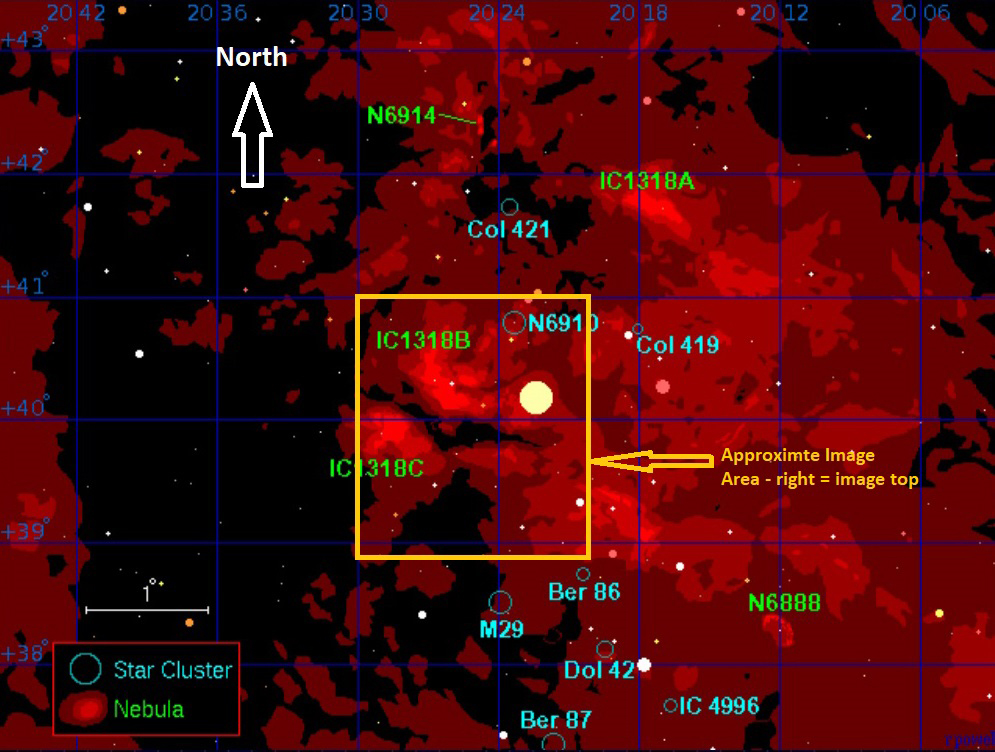
Discovered by Harold Lower and his son Charles in 1939, SH2-261 or Lower’s Nebula is located in the outer regions of the Orion constellation, which is visually between Betelgeuse and Propus in Gemini, on the border of the galactic region between the Orion and Perseus arms of the Milky Way. Mainly consisting of ionized hydrogen, it’s surprising that this interesting, quite large but faint object does not get more attention from astrophotographers, who are perhaps too busy collecting photons from the more famous objects of Orion elsewhere?
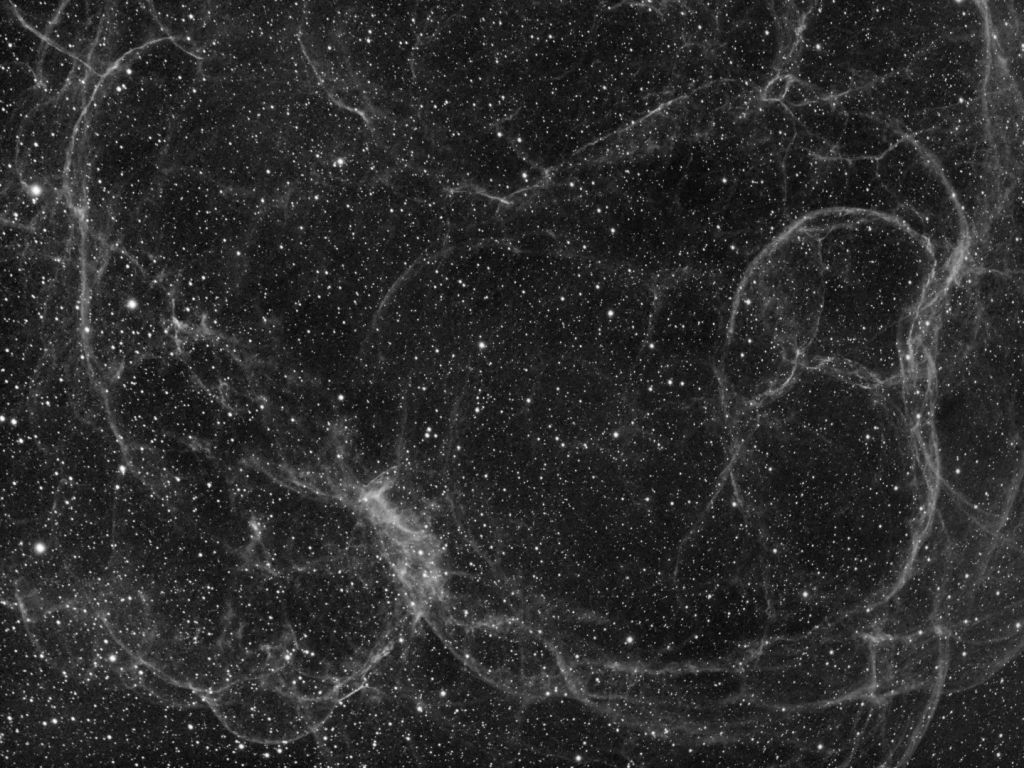
Unusually clear skies were plentiful here at Fairvale Observatory during January, which allowed for some 17-hours integration time, albeit mostly accompanied by a waxing to full moon. The data lends itself to various processing approaches and I played around for a long while with different combinations, in the end favouring an SHO + HOO blend as the main image (see top of the page) and am pleased with the very interesting result; for comparison other bassic versions (HOO & Ha) are shown below.

The aforesaid HII ionized gas is thought to be energised by the runaway bright star HD41997 situated at the centre, adjacent to a mysterious small bluish triangular object and a much fainter blue bubble, seen better elsewhere in higher resolution images. Moreover, catalogued and encompassed within SH2-261 are LBN 862 and LBN 864 and several dark nebulae, which would also require greater magnification (focal length and aperture) to achieve finer detail.
Like most astronomers I’m routinely drawn towards Orion’s famous and rightly popular objects such as M42 the Great Orion Nebula, the Flame Nebula and B33 the Horsehead Nebula, M78 reflection nebula, Barnard’s Loop and other jewels found in and around the central region of the Orion constellation. However, taking a wider perspective, literally and figuratively, the area contains other riches that are too easy to overlook and form good alternative imaging targets at this time of the year – time taken to identify such hidden treasures can be rewarding – in this case thanks to the Lower’s family.
| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | SH2-261 Lower’s Nebula |
| Constellation | Orion |
| Distance | 3,200 light-years approx.. |
| Size | Apparent 50 x 30 arc minutes ~ 25 x 13 light years |
| Apparent Magnitud | +10 |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount | SW AZ-EQ6 GT + EQASCOM computer control & Cartes du Ciel |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| + Starlight Xpress Lodestar X2 camera & PHD2 guiding | |
| Camera | ZWO1600MM-Cool mono CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.65o x 2.0o Resolution 2.05”/pix Max. image size 4,656 x 3,520 pix | |
| EFW | ZWO x8 EFW & 31mm Ha OIII SII 3nm filters |
| Capture & Processing | Astro Photography Tool, PHD2, Deep Sky Stacker, PixInsight v1.8.8-12, Photoshop CC v23.2.1, Topaz Denoise |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre RA 06:09:25.245 DEC +15:45:10.754 Right = North |
| Exposures | Ha x44 OIII x33 SII x28 @ 600 secs Total Integration Time: 17hrs |
| @ 139 Gain 21 Offset @ -20oC | |
| Calibration | 5 x 600 sec Darks 15 x Ha, OIII, SII Flats & Flat Darks @ ADU 25,000 |
| Location & Darkness | Fairvale Observatory – Redhill – Surrey – UK Typically Bortle 5-6 |
| Date & Time | 12th 13th 14th 17th & 20th January 2022 @ +18.30h |
| Weather | Approx. 2oC RH >75% 🌙 waxing 50% to Full Moon |