Each year whilst the Earth rotates around the Sun, we are also moving through the Milky Way and the Universe itself. In time, measured by millions of years, the pattern of the night sky will change but for now, measured on a human scale it appears fixed and as a result has become very familiar, so much so that it has formed the basis of navigation for millennia. For astronomers this affect also results in a predictable pattern of changes during the year, so that every 12-months we first anticipate and then revisit old ‘friends’, none more so than the winter night sky which contains some of the most exciting objects of the year.
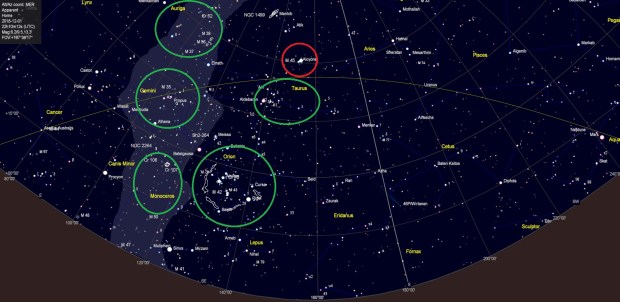 Surprisingly it is possible to obtain an early glimpse of these objects just before dusk at the end of a night’s viewing in the late summer but the real show begins during November, when they start to appear more conveniently in the darkness of the early evening. With this in mind I recently set out to image the vanguard of the winter night sky, Messsier 45 or the Pleiades, an open cluster dominated by bright blue stars. Located at the ‘front’ of the Taurus constellation, this group of stars heralds the arrival of Orion, perhaps the most spectacular and certainly most imaged constellation of the year, followed by Monoceros, Gemini and Auriga with their own wonderful deep sky objects – but first Pleiades.
Surprisingly it is possible to obtain an early glimpse of these objects just before dusk at the end of a night’s viewing in the late summer but the real show begins during November, when they start to appear more conveniently in the darkness of the early evening. With this in mind I recently set out to image the vanguard of the winter night sky, Messsier 45 or the Pleiades, an open cluster dominated by bright blue stars. Located at the ‘front’ of the Taurus constellation, this group of stars heralds the arrival of Orion, perhaps the most spectacular and certainly most imaged constellation of the year, followed by Monoceros, Gemini and Auriga with their own wonderful deep sky objects – but first Pleiades.
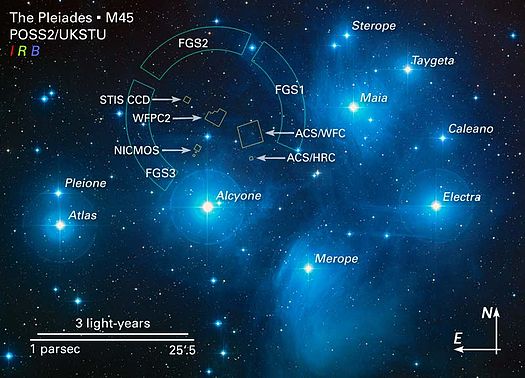
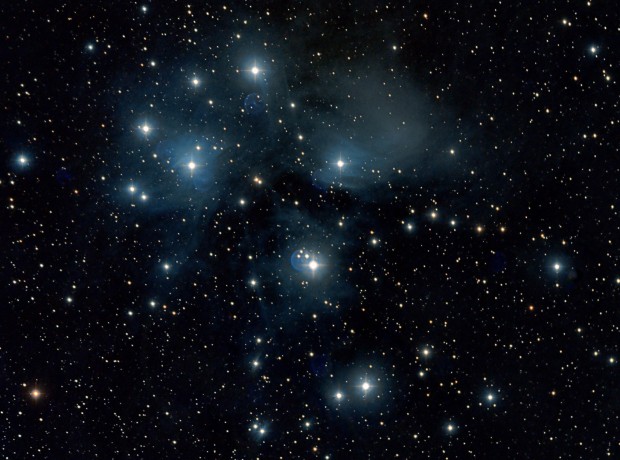
The Pleiades star cluster is visible from almost every part of the globe, from the North Pole to beyond the southernmost tip of South America. The cluster consists of over 1,000 young stars, although only 14 can be seen with the naked eye, of which seven make up the Pleiades asterism or so-called Seven Sisters. The Sisters can usually be seen in light polluted skies but in a dark sky, such as I recently experienced at the Les Granges Observatory in southern France, they form a very distinct group of brilliant stars that literally seem to pierce the blackness of the night sky (top-centre image below).
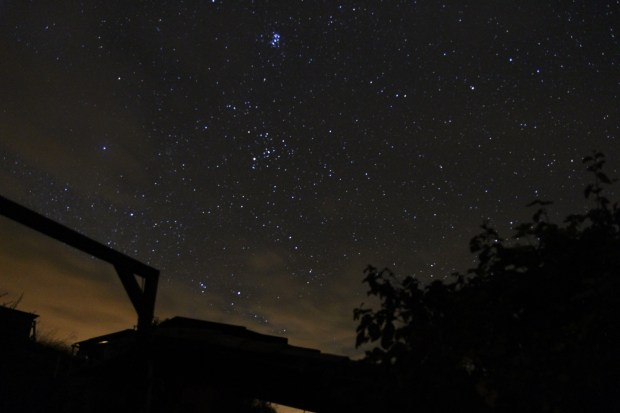

I have successfully imaged the Pleiades before with a DSLR camera but this was the first serious attempt to capture their elusive charm with a more sensitive mono camera. When imaging the Sisters the objectives are two-fold – to capture: (i) their brilliance and colour, and (ii) the delicate interplay of their light illuminating the interstellar gas and dust behind which they are currently moving. It is this latter effect that forms their characteristic signature which differentiates them from other open star clusters.
Given the brightness of the Pleiades stars I chose short 60-second LRGB exposures at Unity setting. Such is the subtle nature of the interstellar illumination against the intensity of the large, bright Pleiades stars, that post-processing needs to be especially careful in order to tease out the contrasting nature of the two features. The result is a beautiful image (top-of-the-page) that captures the power and beauty of this special group of stars which precedes Orion later in the evening at this time of the year and which with luck, will once again provide further exciting opportunities as we continue to move through the rich period of the winter night sky of which the appearance of Pleiades foretells.
| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | M45 Pleiades |
| Constellation | Taurus |
| Distance | 444 light-years |
| Size | 110’ |
| Apparent Magnitude | +1.6 |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount | SW AZ-EQ6 GT + EQASCOM computer control |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| + Starlight Xpress Lodestar X2 guide camera & PHD2 control | |
| Camera | ZWO1600MM-Cool (mono) CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.65o x 2.0o Resolution 2.05”/pix Max. image size 4,656 x 3,520 pix | |
| EFW | ZWOx8 + ZWO LRGB & Ha OIII SII 7nm filters |
| Capture & Processing | Astro Photography Tool + PS2, Deep Sky Stacker & Photoshop CS2, HLVG |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre RA 03:47:06 DEC 24:13:04
Top = North West |
| Exposures | 50 x 60 sec L & 45 x 60 sec RGB (Total time: 185 minutes) |
| @ 139 Gain 21 Offset @ -20oC | |
| Calibration | 15 x 60 sec Darks 20 x 1/4000 sec Bias 10 x Flats LRGB @ ADU 25,000 |
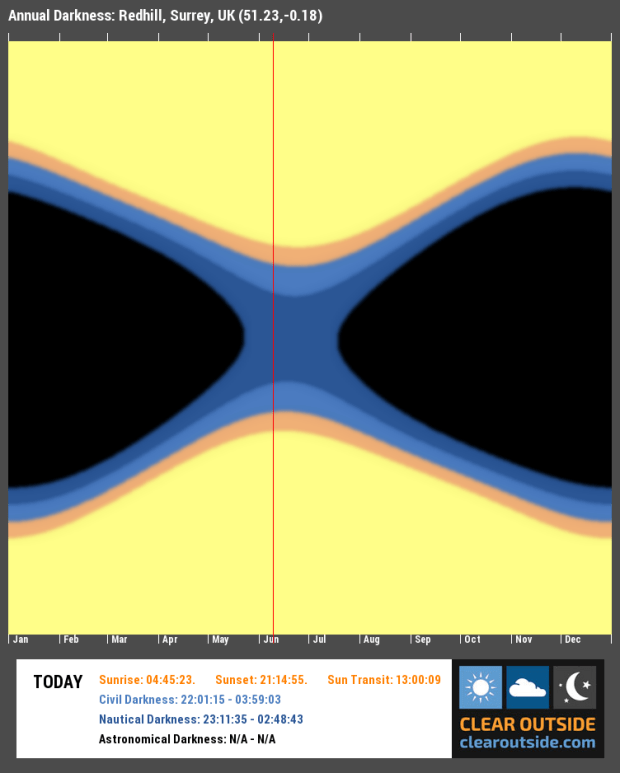
| Location & Darkness | Fairvale Observatory – Redhill – Surrey – UK Typically Bortle 5 |
| Date & Time | 17th November 2018 @ +21.30h |
| Weather & Moon | Approx. 6oC RH <=80% 🌙 Half Waxing Gibbous |