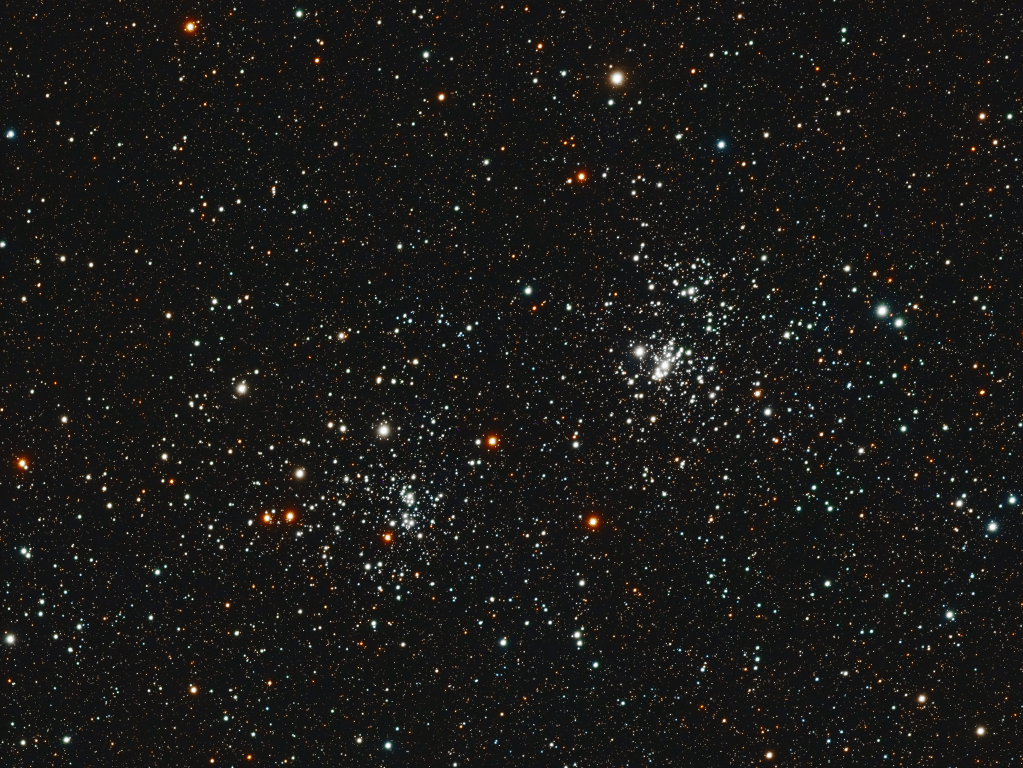
Astronomy is full of surprises, and learning of the mere existence and nature of globular clusters was a revelation to me. Perhaps less spectacular and much younger but no less interesting and attractive are open clusters. The so-called Double Cluster is something of a highlight of autumn and winter skies that I had not, until now imaged; not by neglect but because until recently moving to Somerset my previous view of the north sky in Surrey was completely obscured by my house! Their combined luminosity makes the Double Cluster visible to the naked eye from dark locations, appearing as a hazy patch to the east of the Cassiopeia constellation and are excellent imaging objects too.
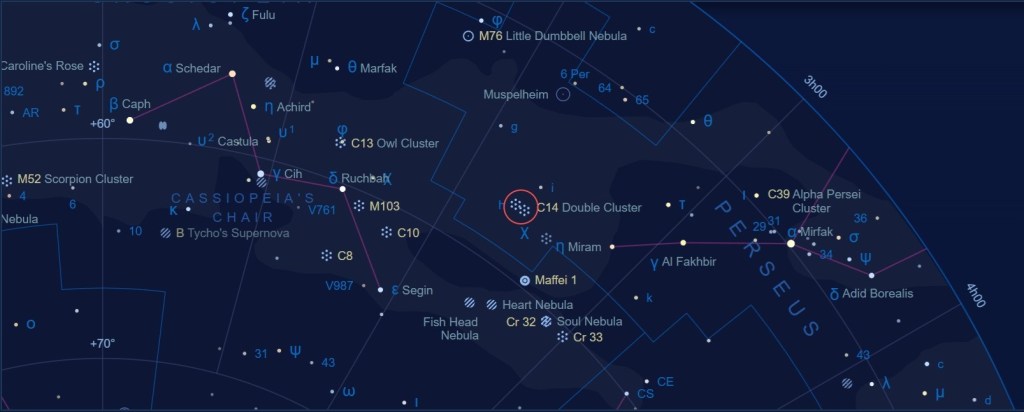
NGC 869 and NGC 884, known as the Double Cluster or h and χ (chi) Persei, is one of the most striking celestial pairings visible in the northern sky. Located in the Perseus spiral arm of the Milky Way, these two open star clusters are located about 7,500 light-years away but separated by only a few hundred light-years. Their proximity, similar age, and shared motion through space suggests that they formed from the same giant molecular cloud, making them a physically associated pair rather than a chance encounter.
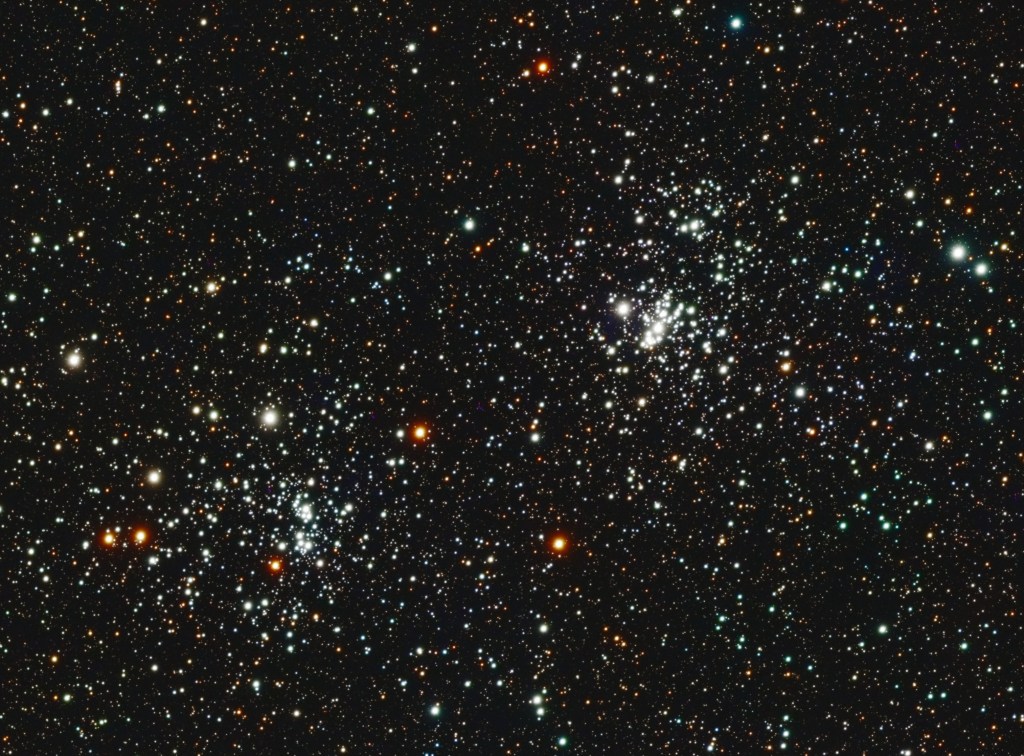

Each cluster contains thousands of stars*, many of which are hot, blue and massive, thereby indicating an early stage of stellar development; estimates indicate an age of approximately 12 to 14 million years. Their youth explains the abundance of B-type and even O-type stars—stellar heavyweights that shine intensely but live only briefly.
The resulting image shows the Double Cluster as a dazzling field of stars. NGC 869, slightly denser and more compact, contains a bright core of hot blue stars. In contrast, NGC 884 appears more loosely concentrated, with a distinctive scattering of bright stars across its central region. Both clusters show subtle hints of red and orange from K-type supergiant stars, evidence that even at their youthful age, some massive stars have already begun to leave the main sequence.
*processing software identified 22,000 stars in the image!
| COMPARISON: GLOBULAR v OPEN CLUSTERS | ||
| Feature | Globular Clusters | Open Clusters |
| Typical Stars | Old, metal-poor | Young, metal-rich |
| Number of Stars | 10⁵–10⁶+ | 10²–10³ |
| Shape | Spherical, dense | Irregular, loose |
| Location | Galactic halo | Galactic disk |
| Age | 10–13 billion years | 1 million–few billion years |
| Longevity | Very long-lived | Short-lived (astronomically) |
| Image Details | |
| Object | The Double Cluster NGC 869 & NGC 884 |
| Constellation | Cepheus |
| Distance | 7,500 light-years |
| Size | 60 arc minutes (each 70 light-years) |
| Apparent Magnitude | +3.8 |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount & Control | ZWO AM5 + ASIair |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| + ZWO 120MM Mini | |
| Camera | ZWO ASI294MM CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.87o x 1.96o Resolution 2.50”/pix Max. image size 4,144 x 2,822 pix | |
| EFW | ZWOx8 EFW & 31mm Chroma Ha, OIII, SII 3nm & RGB filters |
| Capture & Processing | ASIair & PixInsight v1.9.3 Lockhart |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre = RA 02:20:32.57 DEC +57:12:56.0 Top Left = North |
| Exposures | L x 21 + R x 28 + G x 28 B x 24 @ 120 sec + Total Integration Time: 3hr 22 min |
| @ Gain 120 & 30 Offset 21 @ -15oC | |
| Calibration | 10 x 120 sec Darks + 20 x LRGB Flats & Dark Flats @ ADU 32,000 |
| Location & Darkness | Castle Farm Observatory, Wookey, Somerset – UK Typically Bortle 4 |
| Date & Time | 25th November 2025 @ +18.30h |
| Weather | Approx. ❤oC RH >=<80% 🌙 New Moon |