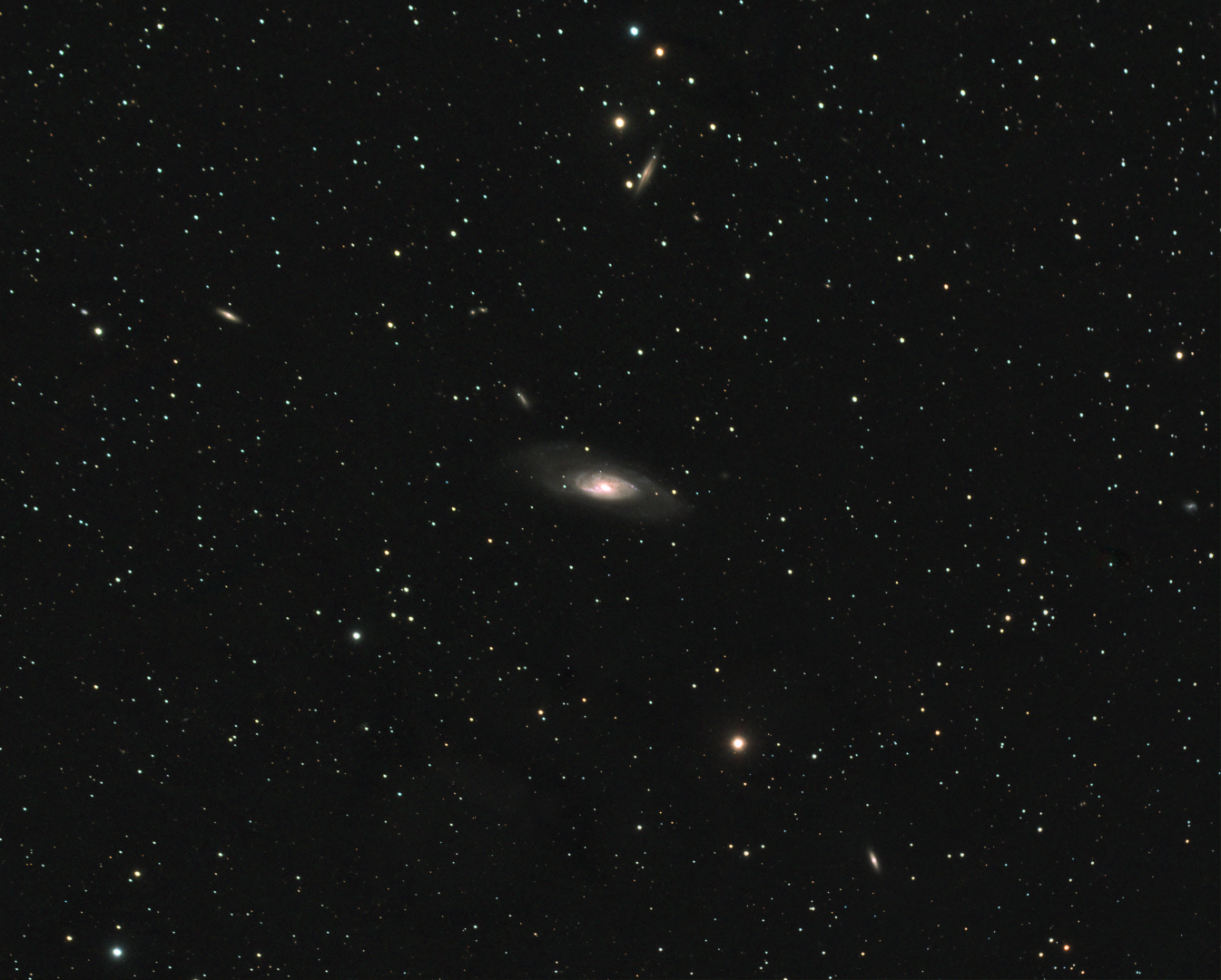
Following a very poor winter period, spring has been nothing less than spectacular and provided many clear nights for astronomy, ironically made all the better by the covid-19 lockdown. With the near absence of road traffic and especially aircraft – Fairvale Observatory is badly affected by flights from nearby Gatwick, Heathrow and Redhill aerodrome – it has resulted in noticeably better seeing, as well as a quieter and more enjoyable environment overall; it’s worth noting that after experimenting with Deep Sky Stacker (DSS), increasing the Kappa-Sigma clipping parameter from 2.0 to 2.50 for the light subs, in all but the worst cases eliminated aircraft tracks in the final stacked image. Resulting from these favourable conditions, I’ve recently been able to image four otherwise difficult targets, amounting to some 40-hours total integration time, literally unprecedented conditions in the +30 years I’ve lived here.
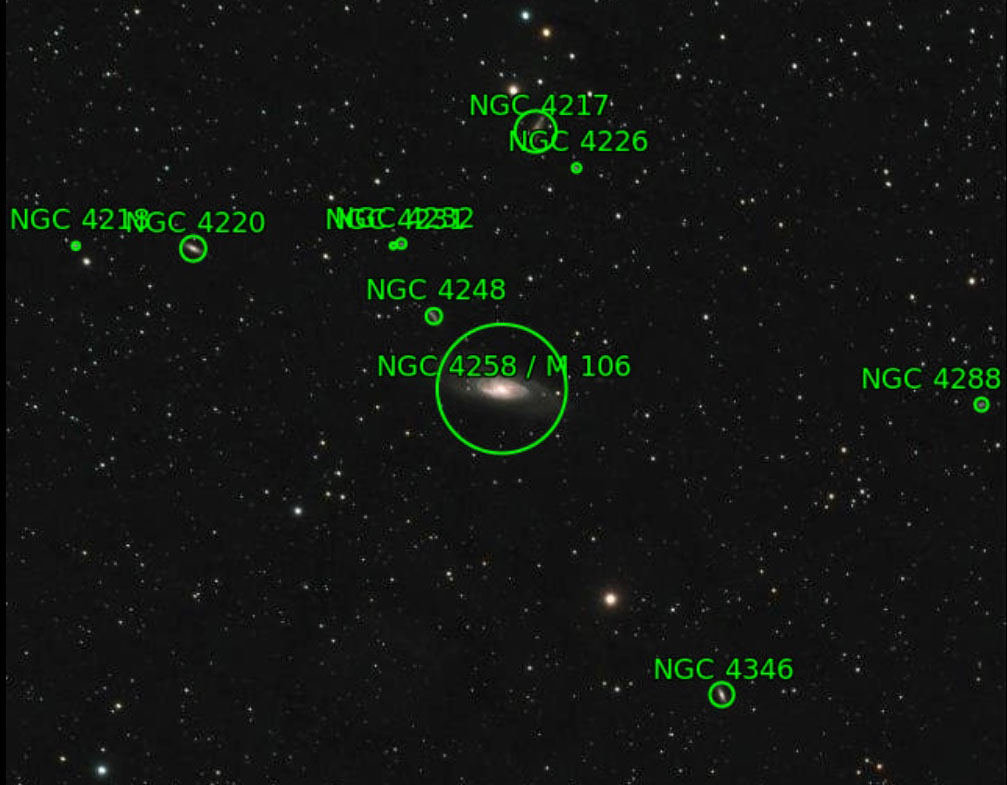
Apart from a brief diversion imaging the Leo Triplet, my attention has otherwise been centered on the constellation of Canes Venatici, AKA the Hunting Dogs. At this time of the year the constellation starts to come into view high overhead from the east at about 10 p.m. and crosses the meridian about three hours later. Located below Ursa Major and above Bootes, the relatively small Canes Venatici hosts five Messier objects, four of which are galaxies and it is these I’ve been drawn to. From earlier test shots I determined that the M94 galaxy was unlikely to be suitable for my equipment but I did obtain and have already described images of first M106 and then M63. Notwithstanding, I had unfinished business with the last of the four galaxies, which I therefore now turned to.
In 2019 I was pleased to acquire my first ever image of the wonderful M51Whirlpool Galaxy and its smaller companion, NGC 5195. However, I noted then that the final LRGB image still needed much more integration time than just 2hr 18min. achieved, plus the addition of Ha-subs and that I hoped to return to the Whirlpool and its neighbour as soon as possible for this purpose.
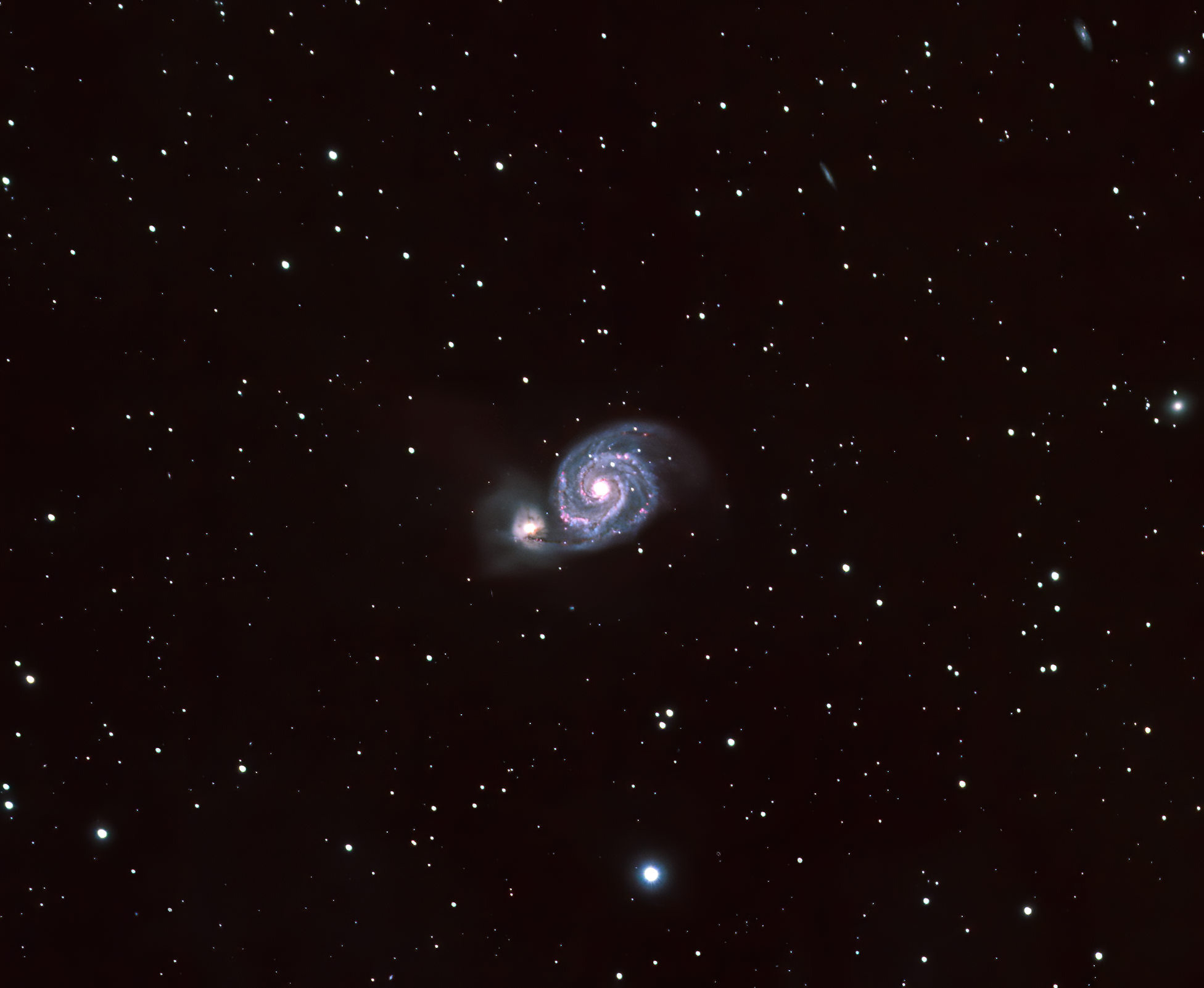

It was therefore a great pleasure to image M51 over no less than seven nights in March and April this spring, which combined with last year’s data resulted in over 16 hours integration time, substantially longer than any previous image I’ve compiled before. Moreover, the quality of seeing also benefitted SNR and guiding quality, thus achieving RMS errors of at least 0.80 arc seconds or better. I did encounter some plate solving issues and had to resort to manual framing on a few nights but fortunately DSS software dealt with alignment OK and the final image is all I could have hoped for (see above + top-of-the-page cropped). Naturally the interaction of the two galaxies is the signature feature of this image but it is the improvement in general colour, detail and addition of Ha-subs highlighting regions of new star formation, that have been most transformative in portraying these objects in all their glory.
Using my current set-up it seems unlikely that the image would benefit significantly from any further data acquisition but I’d like to think I’ll return another day using a larger telescope and higher resolution with which to capture and enjoy even more detail of all these exciting objects of Canes Venatici. It is said that “it’s an ill wind that blows no good” and I am doubtful we’ll ever have such good conditions here again but for now I was delighted to be able to positively exploit this otherwise difficult time in lockdown.
| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | M51 The Whirlpool Galaxy & NGC 5951 |
| Constellation | Canes Venatici |
| Distance | 23 million light-years |
| Size | 11.2’ x 6.9’ 77,000 light-years (M51 only) |
| Apparent Magnitude | +8.4 |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount | SW AZ-EQ6 GT + EQASCOM computer control & Cartes du Ciel |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| + Starlight Xpress Lodestar X2 camera & PHD2 guiding | |
| Camera | ZWO1600MM-Cool mono CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.65o x 2.0o Resolution 2.05”/pix Max. image size 4,656 x 3,520 pix | |
| EFW | ZWO x8 ZWO LRGB & Ha OIII SII 7nm filters |
| Capture & Processing | Astro Photography Tool + PHD2 + Deep Sky Stacker & Photoshop CS3 |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre RA 13:30:03 DEC 47:11:43 (approx.) Top = South Bottom = North |
| Exposures | L x 95 R x 62 G x58 B x 66 Ha x 46 = 327 x 180 sec Total Integration Time: 16hr 21 minutes |
| @ 139 Gain 21 Offset @ -20oC | |
| Calibration | 10 x 180 sec Darks 20 x 1/4000 sec Bias 10 x HaLRGB Flats @ ADU 25,000 |
| Location & Darkness | Fairvale Observatory – Redhill – Surrey – UK Typically Bortle 5-6 |
| Date & Time | 10th April 2019 +23rd 24th 25th 27th March & 20th 21st 22nd April 2020@ +22.00h |
| Weather | Approx. 6oC RH <=60% 🌙 New Moon approx. |