The first galaxies were identified in the 17th Century by the French astronomer Charles Messier, although at the time he did not know what they were. It was only when in 1924 American astronomer Edwin Hubble measured the distance to the Andromeda galaxy using cepheid variables, that the existence of other galaxies was finally established. One hundred years on it’s now estimated that there are between 200 billion and 2 trillion galaxies in the Universe; as Douglas Adams said in the Hitchhikers Guide to the Galaxy, “Space…….is really big”!
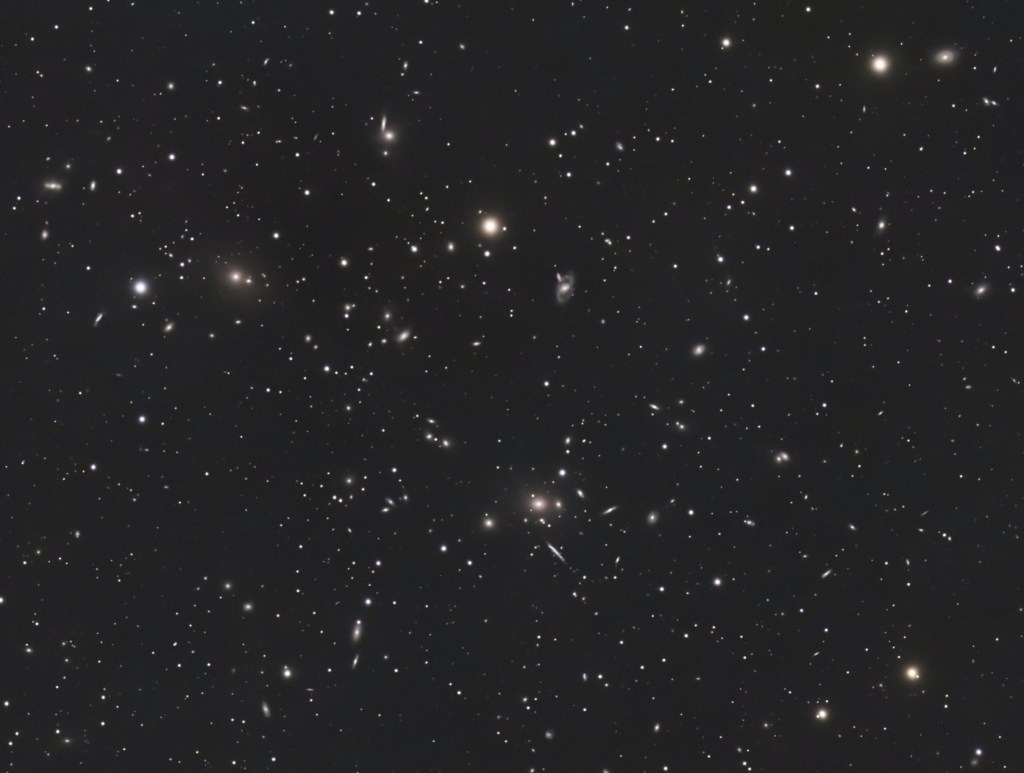
For astronomers this time of the year is generally referred to the ‘Galaxy Season’, as our view of the Milky Way from Earth changes from the winter sky of the Orion Spur and Perseus Arm to the summer view with Cygnus overhead down to Sagittarius in the south, in between we’re looking into deep space. With very few exceptions, galaxies are located very far from Earth, which from our perspective makes them small and therefore a challenge for my imaging equipment. However, this Spring I’ve been imaging the spectacular Leo Galaxy Cluster, a mere 330 million light-years from Earth (see cropped version of cluster at the top of the page).

Containing at least 70 major galaxies, the Leo Cluster unusually consists mostly of spiral galaxies, which are best seen here cropped from the original widefield image. The bright elliptical galaxy near the centre of the image, NGC 3842, has one of the largest known black holes in the universe, which is about 10 billion times more massive than our sun!

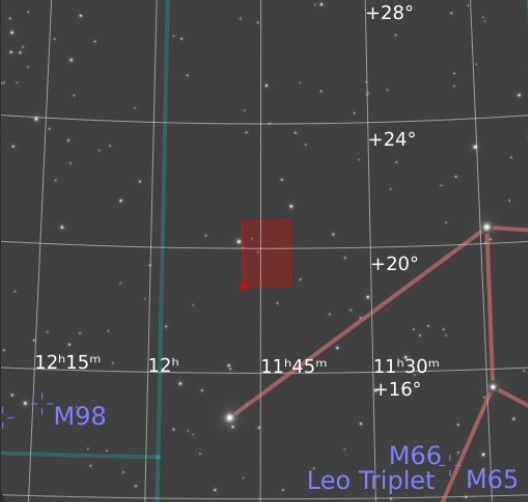
We have come a long way since Galileo Galilei published his astronomical treatise Sidereus Nuncius AKA Starry Messenger in 1610, the first scientific publication based on observations made through a telescope. Galileo’s work completely changed the way humanity understood the night sky and, by extension, our place in space, later leading to the acceptance of the heliocentric model of the planets. Profound as that was, our understanding of the Universe since 1924 has even greater implications. Moreover, the ability for an amateur to image something like the Leo Cluster from my back garden is exciting and very rewarding (see widefield version above + image location + orientation where the red dot = top left of image).
| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | Leo Galaxy Cluster |
| Constellation | Leo |
| Distance | 330 million light-years |
| Size | Various |
| Apparent Magnitude | Various |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount | SW AZ-EQ6 GT + EQASCOM computer control & Cartes du Ciel |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| + Starlight Xpress Lodestar X2 camera & PHD2 guiding | |
| Camera | ZWO ASI294MM CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.87o x 1.96o Resolution 2.50”/pix Max. image size 4,144 x 2,822 pix | |
| EFW | ZWOx8 EFW & 31mm LRGB filters |
| Capture & Processing | Astro Photography Tool (APT), Deep Sky Stacker & PixInsight v1.8.9-2 |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre = RA 11:44:12.40 DEC +19:50:25.70 Right = North |
| Exposures | L x30 + R x31 + G x31 + B x 31 @ 180 sec Total Integration Time: 6hr 9min |
| @ Gain 120 & 30 Offset 21 @ -15oC | |
| Calibration | 10 x 180 sec Darks + 10 x BB Flats & Dark Flats @ ADU 32,000 |
| Location & Darkness | Fairvale Observatory – Redhill – Surrey – UK Typically Bortle 5-6 |
| Date & Time | 7th + 9th + 14th April 2024 @ +21.30h |
| Weather | Approx. <9oC RH >=65% 🌙 >=0% New Moon Waxing |