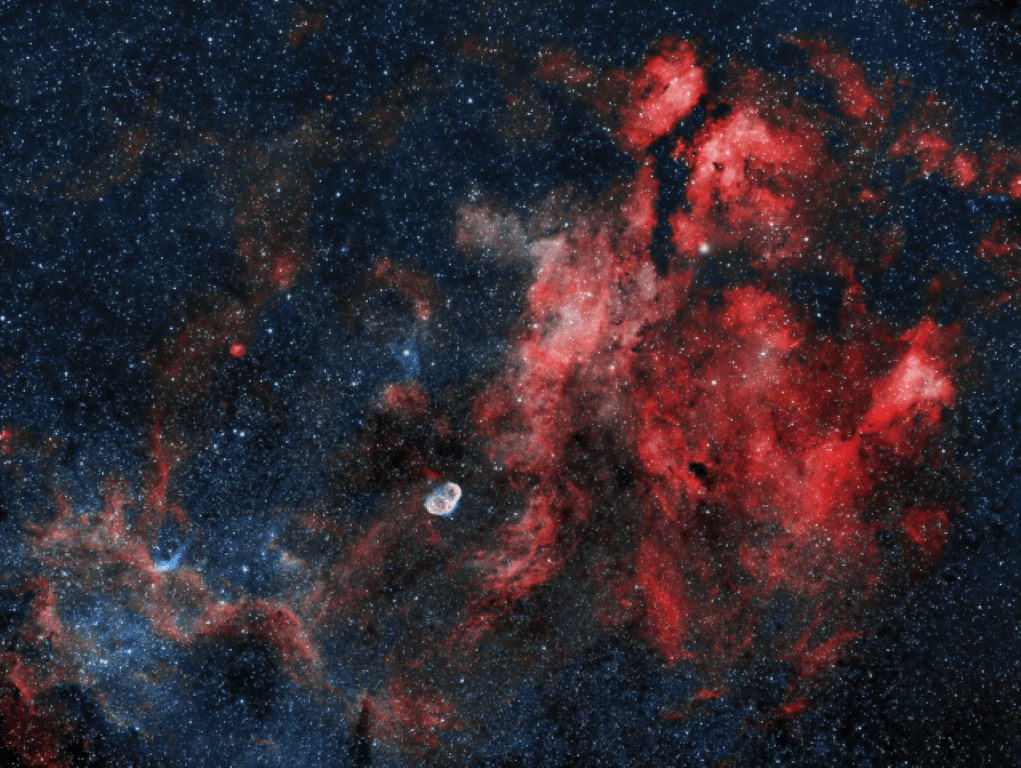
Hitherto, most of my astrophotography has concentrated on a variety of specific objects that work within the 2.65o x 2.0o field-of-view provided by the combination of my William Optics GT81 refractor and ZWO ASI1600MM-Cool camera. After recently pairing the aforesaid ZWO mono camera with a Samyang 135 lens (often marketed elsewhere as the Rokinon 135) my astrophotography world has expanded dramatically to an enormous 7.50o x 5.67o, some x8 larger than before. As a result, this excellent lens that also captures great detail, provides new opportunities to image some of the very large features that abound throughout the Universe without having to resort to a mosaic imaging; this a great advantage when working in UK weather conditions which usually provides less imaging time than required.
In this case I chose to frame the image in such a way as to encompass some familiar objects, such as the Butterfly Nebula (IC1318) and the Crescent Nebula (NGC6888) anchored by Sadr, the yellow-white supergiant star that stands out from within the very large Cygnus-X region. Processed here in HOO, with 6-hours integration time and full calibration (darks, flats & flat darks), the final image provides a magnificent view of this large, interesting region that augurs well for future widefield imaging with this new rig. I’m particulalry intrigued by the bluish feature at about 8.0 o’clock of the Crescent Nebula, which I now believe to be associated with WR-134: a bubble-like structure some 50 light-years in diameter consisting of OIII rich light formed by an intense wind emanating from the Wolf-Rayet star at it’s centre. The breadth of view it provides can encompass myriad of objects in exceptional detail, thereby providing a wider context that is simply awe-inspiring to see – it’s just like shrinking the Universe!

| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | Sadr Region |
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Distance | +5,000 light-years |
| Size | Full FOV – see below |
| Apparent Magnitude | +/- 7.0 |
| Scope / Lens | Samyang 135 @f2.8 |
| Mount | SW AZ-EQ6 GT + EQASCOM computer control & Cartes du Ciel |
| Guiding | Sky-Watcher EvoGuide 50ED |
| + Starlight Xpress Lodestar X2 camera & PHD2 guiding | |
| Camera | ZWO1600MM-Cool mono CMOS sensor |
| FOV 7.5o x 5.67o Resolution 5.81”/pix Max. Image Size 4,656 x 3,520 pix | |
| EFW | ZWOx8 EFW & 31mm ZWO LRGB & 7nm Narrowband filters |
| Capture & Processing | Astro Photography Tool + PHD2 + Deep Sky Stacker, PixInsight v1.8.8-12, Photoshop CC, Topaz Denoise |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre RA 20:16:40.452 DEC +38:50:14.404 Right = North Top = East |
| Exposures | 36 x 500 sec Ha, 36 x 300 sec OIII Total Integration Time: 6hr |
| @ 139 Gain 21 Offset @ -10oC | |
| Calibration | 5 x 300 sec Darks 15 x Flats & Flat Darks |
| Location & Darkness | Fairvale Observatory – Redhill – Surrey – UK Typically Bortle 5-6 |
| Date & Time | 10th & 12h August 2022 @ +22.00h |
| Weather | Approx. 25oC RH 50 – 60% 🌙 100% Full Moon |
