For good reason spring is known as “galaxy season” by astronomers but during this period, shortly before astronomical darkness inevitably disappears for summer, there’s also another show in town. Closer to home in the denser extremities of our galaxy, over 150 globular clusters have so far been identified orbiting above and below the plane of the Milky Way within the galactic halo. Globular clusters consist of hundreds of thousands of tightly packed stars that are surely one of the more enigmatic features of astronomy, as we now know that similar clusters also are associated with other galaxies throughout the Universe. Whilst the formation of globular clusters is poorly understood, we do know that at 10.0 to 13.5 billion years they are very old. Given their age, location and density, it seems that globular clusters formed under very different circumstances to the more recent dispersed star clusters.

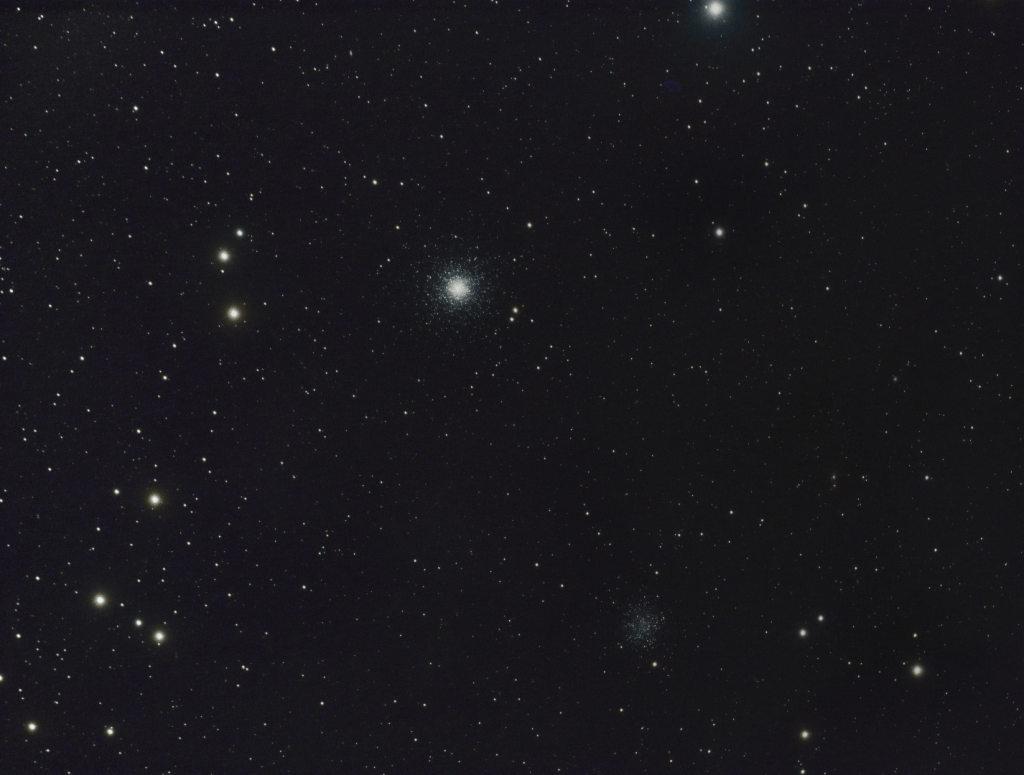
Sagittarius and Ophiuchus brim with globular clusters but at the higher latitude here at Fairvale Observatory it is necessary to view those around the regions of Canes Venatici, Virgo or Coma Berenices; the Great Cluster of M13 and others such as M92 and NGC 6229 located in the aforesaid Hercules constellation move into a better view later during early summer. Having previously imaged a number of these clusters in the past, this spring I looked around for something new and different, which I found in the name of M53 (Above + left of centre – main image top of the page) . In this case it turned out to be two for the price of one, as with careful framing it was possible to include a second globular cluster, NGC 5053 (Below + right of centre – main image top of the page).

Located in the southern area of the Coma Berenices constellation, M53 (Above left of centre – main image, top of the page) is some 58,000 light years from Earth. Containing some 500,000 metal-poor stars, the cluster equates to 13 arc minutes of sky or about 220 light years in diameter, with an estimated age of 12.67 billion years. Just over 1o east of M53, NGC 5053 is 53,500 light-years away, with an apparent size of 10.5 arc minutes or 160 light-years. Although classified as a globular cluster, NGC 5053 is more irregular and dispersed in nature without a distinct bright core and is therefore dimmer than its neighbour, making it more difficult to image.
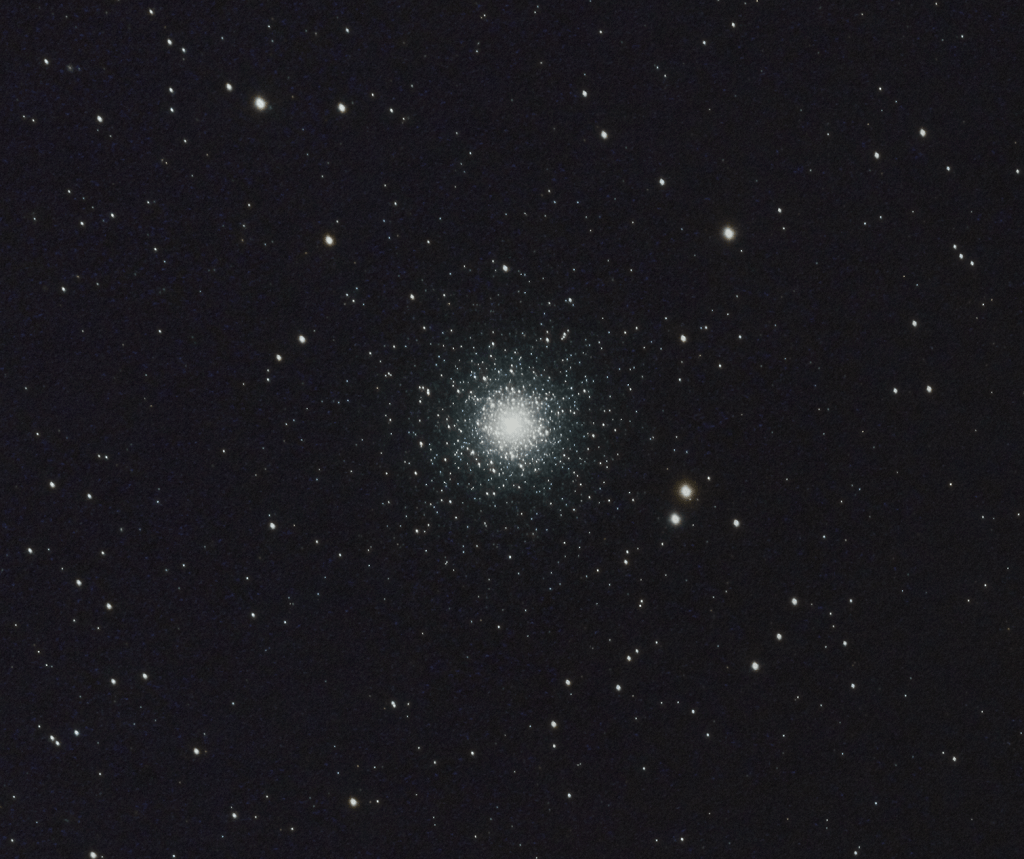

All-in-all I believe these two globular clusters, combined with the star studded background that just includes the binary Diadem star (Upper edge + right of middle – main image, top of the page) southwest of M53, altogether makes for a rich and interesting final image.
| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | M53 & NGC 5053 |
| Constellation | Coma Berenices |
| Distance | Approx.. 58,000 & 53,000 light-years |
| Size | 13.0 & 10.5 arc minutes |
| Apparent Magnitude | +8.33 & +10.00 |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount | SW AZ-EQ6 GT + EQASCOM computer control & Cartes du Ciel |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| + Starlight Xpress Lodestar X2 camera & PHD2 guiding | |
| Camera | ZWO1600MM-Cool mono CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.65o x 2.0o Resolution 2.05”/pix Max. image size 4,656 x 3,520 pix | |
| EFW | ZWOx8 EFW & 31mm Chroma LRGB filters |
| Capture & Processing | Astro Photography Tool + PHD2 + Deep Sky Stacker, PixInsight v1.8.8-7, Photoshop CS3, Topaz Denoise |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre RA 13:13:59.405 DEC +18:01:48.627 Lower Left Corner = North Top = South West |
| Exposures | 55 x 180 sec L , 34 x 180 sec R, 30 x 180 sec G&B Total Integration Time: 7hr 27 min |
| @ 139 Gain 21 Offset @ -20oC | |
| Calibration | 10 x 60 sec Darks 15 x LRGB Flats & Dark Flats @ ADU 25,000 |
| Location & Darkness | Fairvale Observatory – Redhill – Surrey – UK Typically Bortle 5-6 |
| Date & Time | 13th, 15th & 16th April 2021 @ +21.00h |
| Weather | Approx. <5oC RH >55% 🌙 6% waxing |