I like to think and operate at both ends of the spectrum: sometimes considering detail and its implications and often exquisite beauty, whilst on the other hand taking a wider view will often provide broader insight and answers – notwithstanding, I am usually drawn towards the latter. There was no shortage of scope for such thoughts in my career as a geologist and now as my hobby in astronomy. I have become fascinated with parts of the Universe and captivated by imaging them: galaxies, nebulae, star cluster etc. but the wider view is often even more astounding and perplexing.

My nascent astroimaging has already produced some rewarding photographs, which using the fast William Optics GT81 refractor has enabled me to obtain images of up to 3o FOV. In fact this became something of a theme last year, successfully imaging features such as the Sadr Region and as they say, one thing has led to another. Wanting to image even wider views there’s mostly only one alternative, using a camera and lens. I’ve tried this before, on a tripod and fixed to the ALT-AZ EQ6 mount but with mixed success. Meanwhile, I came across excellent pictures taken using lightweight tracking mounts on a tripod and as a result the way forwards became obvious; after scanning the Classified advertisements online for a while I was fortunate to find and purchase a second-hand Vixen Polarie mount last September.
Probably my favourite object, which can rightly be considered the signature image of the winter night sky and is therefore around at the moment, is the constellation of Orion and especially its numerous and often exciting constituent parts: M42, Horsehead & Flame Nebulae etc. After waiting for weeks for the clouds to clear, I briefly got a chance to image Orion using the Vixen Polarie early in November, whilst at the same time using the WO GT81 to obtain yet another picture of the irresistible Great Orion Nebula M42.

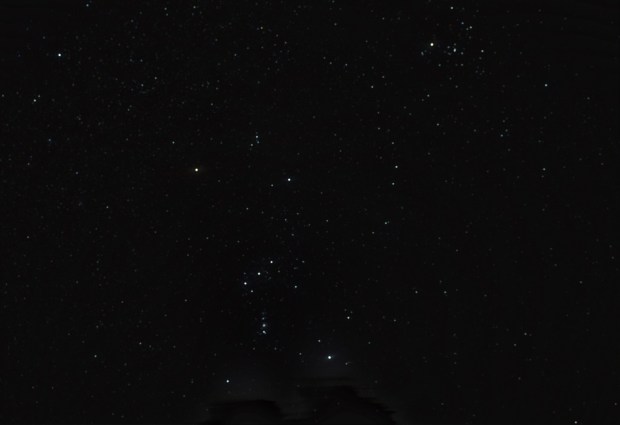
Orion’s Sword – including the wonderful Great Orion Nebula M42 et al : WO GT81 + modded Canon 550D & FF | 14 x 180 secs @ ISO 1,600 | 9th November 2015
The Vixen Polarie is a deceivingly simple and well-made solution to obtaining long exposure images of the wider night sky using a camera and lens. As stability remains essential for the mount and camera to operate at their best, I also purchased a decent Manfrotto tripod and suitable ball heads to attach the Polarie. After that it was simple, well not quite! Trying out the Polarie at the same time as using the GT81 and being first time out was a mistake. I fumbled setting up the equipment and initially even forgot to turn on the tracking, leaving only a short time to grab a few images before the clouds rolled in once again! Not surprisingly the results were mixed and I was left frustrated. With continuing poor seeing conditions, it was to be a further month before I had an opportunity to properly use the Vixen Polarie again – this time with a new Sigma 10 – 20 mm ultra-wide angle lens I had just purchased.

Vixen Polarie & Canon 700D + 18 – 55mm lens | 19 x 60 secs @ ISO 800 | 9th November 2015
Having by now spent more time looking at the manual (we all get there, in the end) and concentrating on imaging using only the Polarie, this time I was able to achieve a good set-up and remembered the correct sequence of operation. As the mount sits high on the tripod I am just about able to see Polaris in a small gap between the roof of my garage and house, something hitherto impossible when using the lower positioned AZ-EQ6 mount. As a result I am able to achieve a reasonably good visual polar alignment, though a polar scope made specifically for the Vixen Polarie would improve this further; probably something for another time? Nevertheless, such an alignment at Fairvale Observatory is a first and was a major breakthrough that has already permitted exposures of 4 minutes and could probably go to 5 to 6 minutes or more.

The high position of the Vixen Polarie on the tripod provides an otherwise elusive view of Polaris between the garage / utility room and the main house for polar alignment, at last! Alignment of the mount is carried out by viewing through the hole in the top right of the Polarie – better alignment can be achieved by using a polar scope which fits through the middle of the Polarie mount.
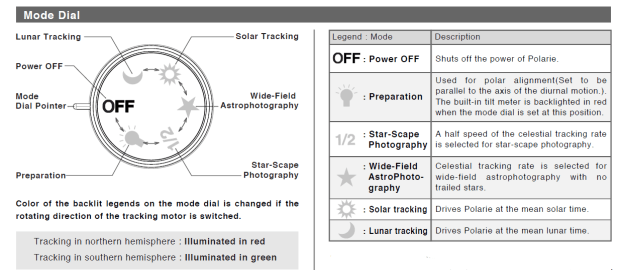
Once polar aligned, fixed on the front of the Vixen Polarie the camera then rotates to follow the celestial sphere and chosen object in order to achieve a sharp image with long exposures. For this purpose there are 4 tracking rates: sidereal, half sidereal, lunar and solar. With no interesting foreground here I concentrated on the sky by using the sidereal rate; for more scenic shots with the landscape incorporated, using half-sidereal provides a compromise in order to achieve a non-blurred image of the sky and landscape, though this method is inevitably limited to shorter exposures than sidereal.

Vixen Polarie mount on Manfrotto tripod – a lightweight, portable tracking method for widefield astroimaging

Vixen Polarie – close-up showing x2 ball head fittings

Vixen Polarie – tracking speed settings

Vixen Polarie with DSLR attached & ultra-wide lens
I have adapted a somewhat basic red dot finder to fit on top of the DSLR camera using the hot shoe, which was immediately helpful to accurately locate the desired target area. However, as previously experienced, once again achieving focus proved quite difficult, basically requiring just trial and error; I intend to look into a more efficient method but in the absence of a Bahtinov mask this is likely to be the best technique for now. A laptop can be used for image capture but maintaining the themes of portability and simplicity, I successfully used an intervalometer to control exposures.
Whilst initially my target was the Orion constellation, I’ve long held the ambition to image Barnard’s Loop, a much larger and elusive feature surrounding the constellation and more difficult to photograph. I had tried this before last January with limited success but ever since acquiring the Vixen Polarie this has been my No1 imaging goal.

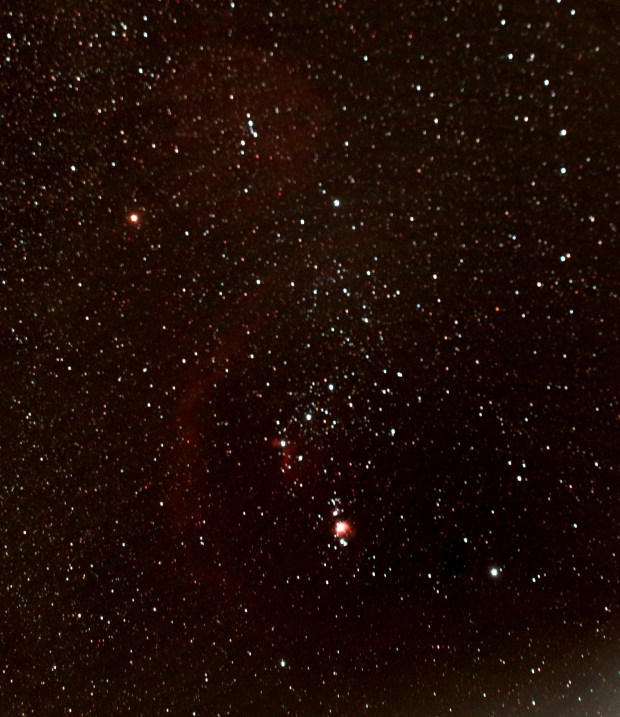
The Orion Constellation & Barnard’s Loop (up / north is left) : AZ-EQ6 Mount + Canon 550D & 200mm Telephoto | 180 secs @ ISO 1,600 & calibration | 22nd January 2015
Unable to see with the naked eye, only using long exposure photography unveils the majesty of Barnard’s Loop, an emission nebula to the left (east) of the Orion constellation. Shaped as a large-C, the loop completely encompasses the eastern side of the constellation and is thought to be a recent supernova front moving out from Orion and illuminated by stars from within the nebula, as well as part of the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. Discovered and named after astrophotographer E. E. Barnard in 1895, at some 14o or 300 million light-years across Barnard’s Loop is enormous; however, the entire Molecular Cloud is about 30o in size!
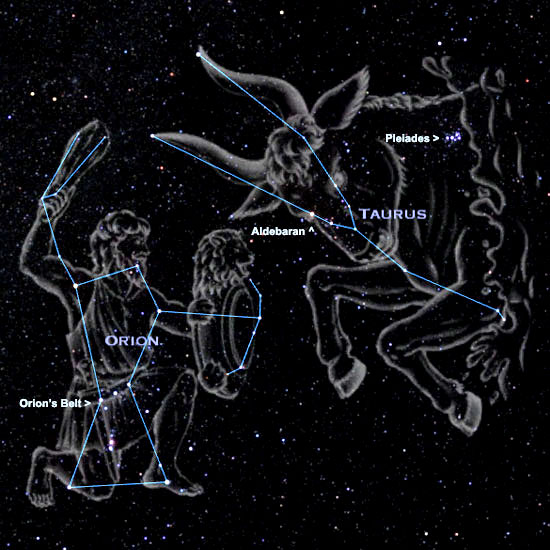
The Orion constellation was originally conceived in Greek mythology as the Hunter, pursuing Taurus the Bull to the west, with the stars tracing out a shape of a hunter holding a shield and club in each hand, a belt around the waste with a sword attached. What they could not have known at the time is that he also has a head, in the form of the Lamda Orionis Nebula (Sh2-264), located centrally and above Betelgeuse and Bellatrix.

Barnard’s Loop & Lamda Orionis Nebula : Vixen Polarie & modded Canon 550D + Sigma UWA @ 20mm | 11 x 240 secs @ ISO 1,600 + darks | 7th January 2016
I was able to image Barnard’s Loop on 7th and 14th January; at ISO 1,600 the first images showed the Loop but certainly left room for improvement, as a result I shot the subsequent images at ISO 800 and obtained a noticeably better outcome – though I had to push post processing to reveal the features. The Loop and head are clearly evident but I’ve been intrigued to see other objects also revealed, albeit without the detail obtained with prime focus imaging using the telescope: Great Orion Nebula, Horses Head & Flame Nebulae and surprisingly on the left (east) of the Loop the Rosette Nebula. Looking at other’s images of Barnard’s Loop it is clear that I will need to take significantly more subs to properly reveal the full beauty of this wonderful and very large feature – dark skies would be nice too – but for the moment I am pleased with my first outing using the Vixen Polarie, which holds great promise for capturing a wider perspective of the Universe.
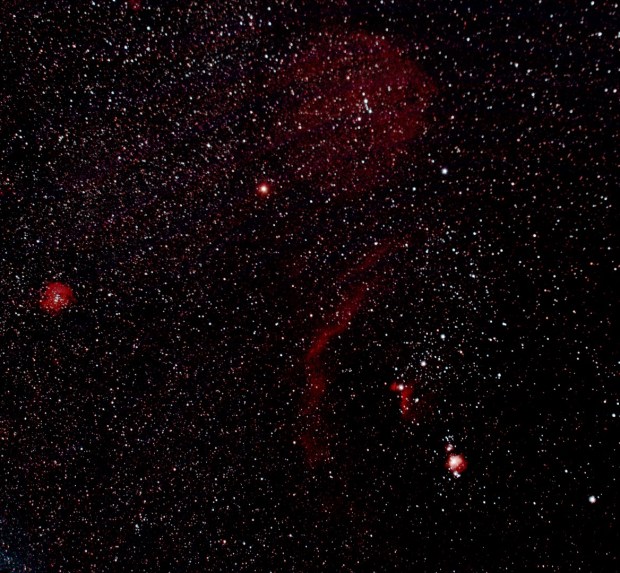

Barnard’s Loop & Lamda Orionis Nebula + Rosette Nebula on far left : Vixen Polarie & modded Canon 550D + Sigma UWA lens @ 20mm | 14 x 240 secs @ ISO 800 | 14th January 2016

Pingback: Fairvale Observatory Part-3, Progress: modded DSLR, EQMOD / ASCOM computer control, autoguiding etc. | WATCH THIS SPACE(MAN)
Pingback: The Sky’s The Limit | WATCH THIS SPACE(MAN)
Pingback: Reflections – 2016 | WATCH THIS SPACE(MAN)