
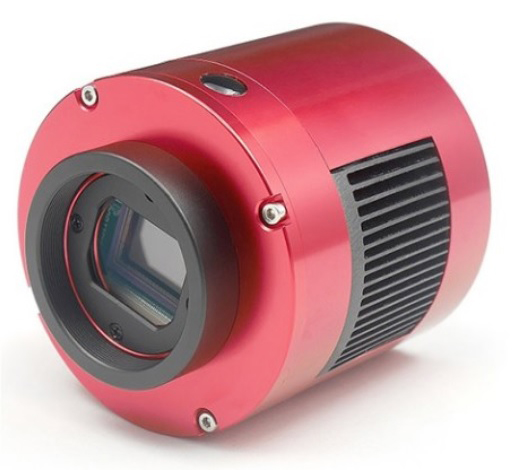
The history of astrophotography will record a period of rapid innovation during the past decade, amongst which one of the stand-out developments has been that of the CMOS sensor based camera, notably the ZWO ASI1600MM-Cool (see below). Just look at any astrophotography website such as Astrobin and it won’t take long to find an image taken with this camera such is its popularity. It is this very camera that I was fortunate to purchase in December 2016 shortly after its release and has been the core of my astrophotography set-up ever since.
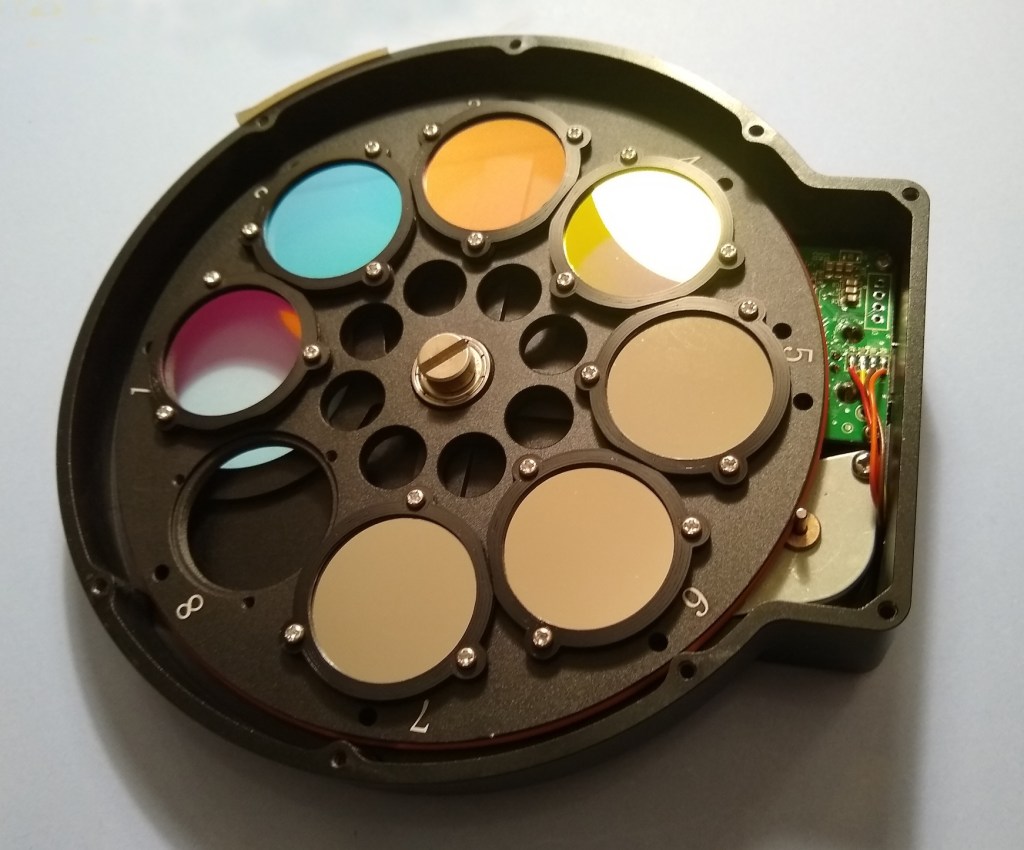
I have generally been very happy with the results achieved with the ZWO camera, although an issue sometimes occurs when imaging large stars, so called ‘star bloating’. There are a number of theories discussed ad nauseam online why this might occur, of which microlensing and / or diffraction seems most likely and probably relates to either – the sensor, sensor cover or filters. Since beginning with the ZWO camera I’ve used their excellent matching EFW with LRGB and 7nm narrowband filters. Notwithstanding, the filters are considered to be somewhat ‘low end’ by the aficionados of such things and after living with the ZWO filters for some time, at considerable cost I recently decided to upgrade to a set of Chroma 31mm filters – LRGB + 3nm narrowband. Together with Astrodon, Chroma filters are generally considered to be the best and my expectations were therefore high.
Being unmounted I’d previously found the ZWO filters tricky to install using the small screws and fibre washers supplied. At 3mm Chroma are physically 1mm thicker than ZWO filters and also need to be fitted in a specific direction, which is ‘letters up’ or with top of the ID letters on the side of the filter facing towards the sensor; this is disputed by the manufacturer but there’s substantial first-hand experience online that suggests otherwise. With these issues in mind I sought out bespoke filter masks and longer M2 6mm screws to hold the thicker filters firmly in place. The 3D printed masks from Buckeyestargazer in the USA did a great job securing the filters and are better than those from ZWO – the internal edge of the mask forms an L-shaped ledge into which the filter fits snuggly. Ready to go, I then had to wait nearly 4-months before the clouds parted to try out these expensive pieces of glass and then it was a full moon – I often wonder if astrophotography is a good hobby to choose in the United Kingdom but it’s too late now?

Given the presence of the moon it therefore had to be suitable narrowband target and after three years since I’d last imaged this object it was an opportunity to have another go at NGC 2244 AKA the Rosette Nebula, though being late February there was limited time each night before the object sunk low behind trees on the western horizon; coincidentally the ZWO ASI1600MM-Cool First Light in early 2017 was also the Rosette. Before starting serious imaging I first tried some test shots to make sure everything worked OK and immediately discovered that the change from 7nm to 3nm had a significant impact on light gathering, thus requiring greater exposure times of an unprecedented 10 minutes. Not surprisingly this was also apparent when taking flats which increased exposure time of up to x10 longer in duration compared to the ZWO filters; conversely preliminary but limited tests on the broadband filters seem to indicate greater transparency and thus shorter exposures, time will tell if this is correct.
So was it all worth it? I’m very pleased with the final image which was processed using the SHO Hubble Palette with PixInsight and Photoshop (see top of the page). There are a number of significant bright stars in and around the Rosette which the Chroma filters have handled well but overall it is the more delicate tone that has been achieved which is most pleasing. Fundamentally the 3nm filters have produced a more subtle quality to the overall image and in particular the nebulosity. In addition, applying Hartmut Bornemann’s excellent colour calibration script AutoColor for the first time (see Visible Dark’s video tutorial here) has resulted in a soft but exciting colour palette.
Subsequently I have focussed on the inner region of the nebula which contains the so-called ‘Carnival of Animals’ (see above), which has been cropped and reprocessed individually to show-off the ‘animals’ or Bok globules – named after the Dutch-American astronomer Bart Bok, who in 1947 proposed that these dark nebula indicated clouds of dust undergoing gravitational collapse as part of the process of new star formation, which has since been confirmed. In conclusion I’d therefore say that despite the obstacles, issues and long wait, on the evidence so far the addition of the Chroma filters to my set-up has been very successful – transformative in fact. Now I wonder if they make something that removes the clouds?
| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | NGC 2244 + 2337 + 2238 + 2239 + 2246 AKA the Rosette Nebula |
| Constellation | Monoceros |
| Distance | 5,200 light-years |
| Size | 65 light-years |
| Apparent Magnitude | 9 |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount | SW AZ-EQ6 GT + EQASCOM computer control & Cartes du Ciel |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| + Starlight Xpress Lodestar X2 camera & PHD2 guiding | |
| Camera | ZWO1600MM-Cool mono CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.65o x 2.0o Resolution 2.05”/pix Max. image size 4,656 x 3,520 pix | |
| EFW | ZWO EFW + Chroma Ha, OIII & SII 3nm filters |
| Capture & Processing | Astro Photography Tool + PHD2 + Deep Sky Stacker & Photoshop CS3 |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre RA 06:31:52.688 DEC 04:58:11.11 Top = North |
| Exposures | 12 x 600 sec Ha & SII 11 x 600 sec OIII Total Time: 5hr 50 min |
| @ 139 Gain 21 Offset @ -20oC | |
| Calibration | 5 x 600 sec Ha + OIII + SII Darks 20 x 1/4000 sec Bias & 15 x Ha + OIII + SII Flats & Dark Flats @ ADU 25,000 |
| Location & Darkness | Fairvale Observatory – Redhill – Surrey – UK Typically Bortle 5-6 |
| Date & Time | 26th 27th 28th February 2021 @ +21.15h |
| Weather | Approx. <5oC RH >=65% 🌙 100% Full Moon |
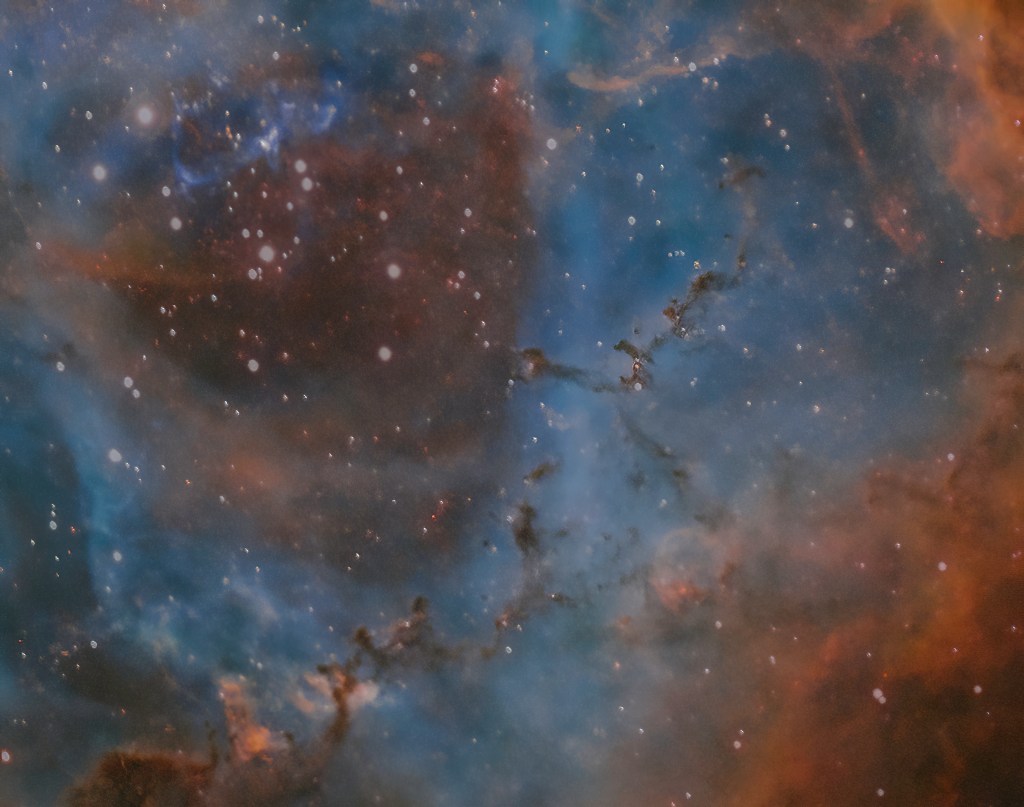
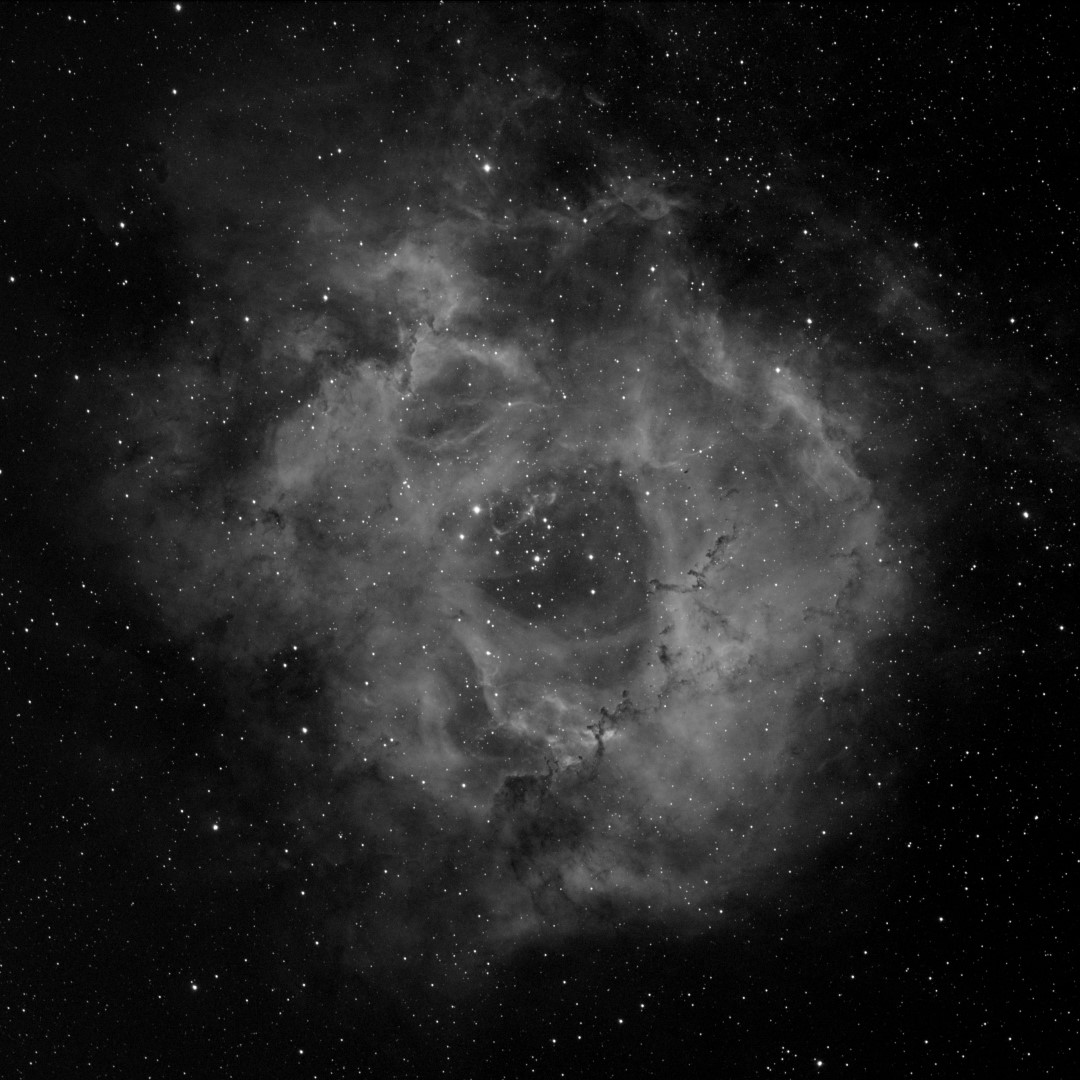
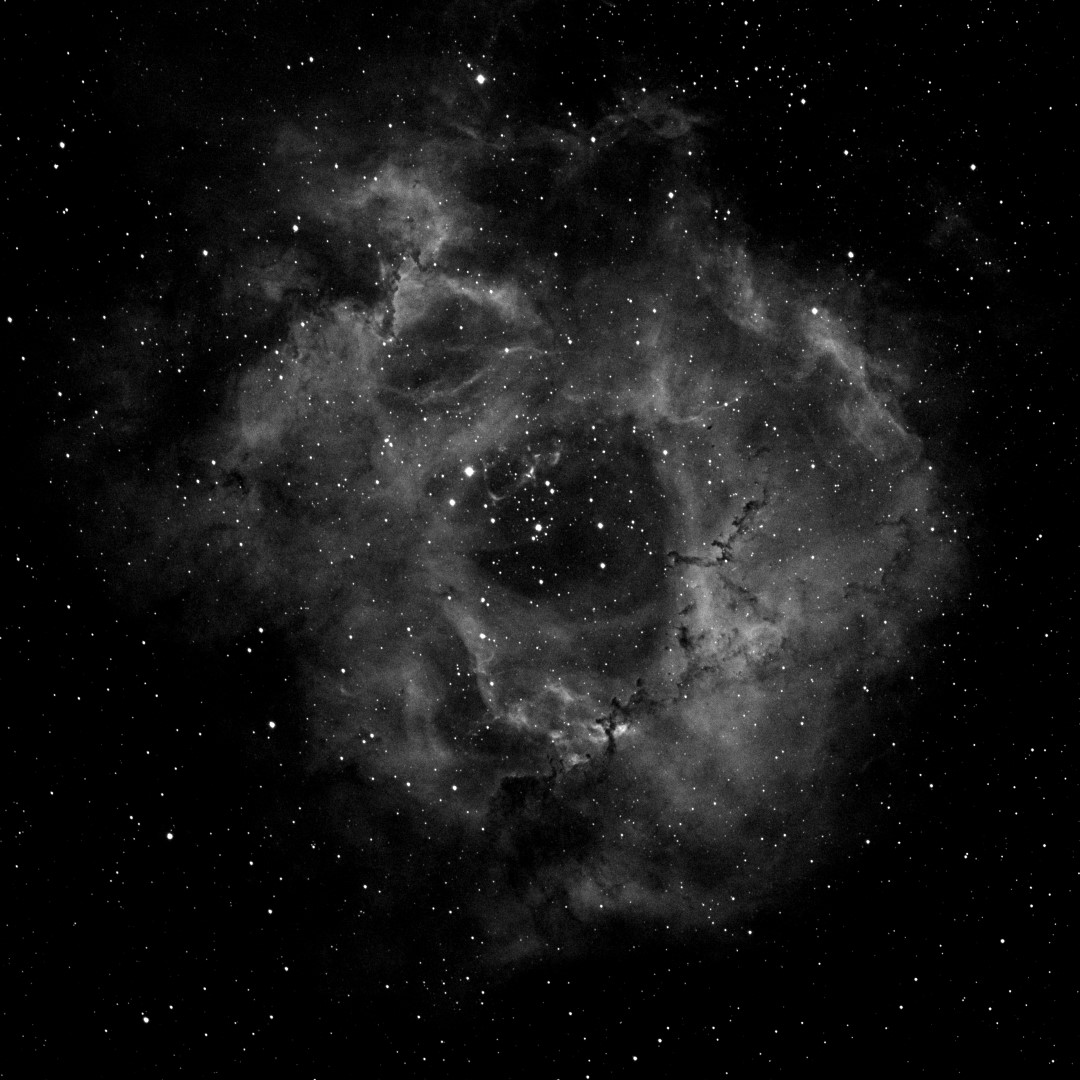
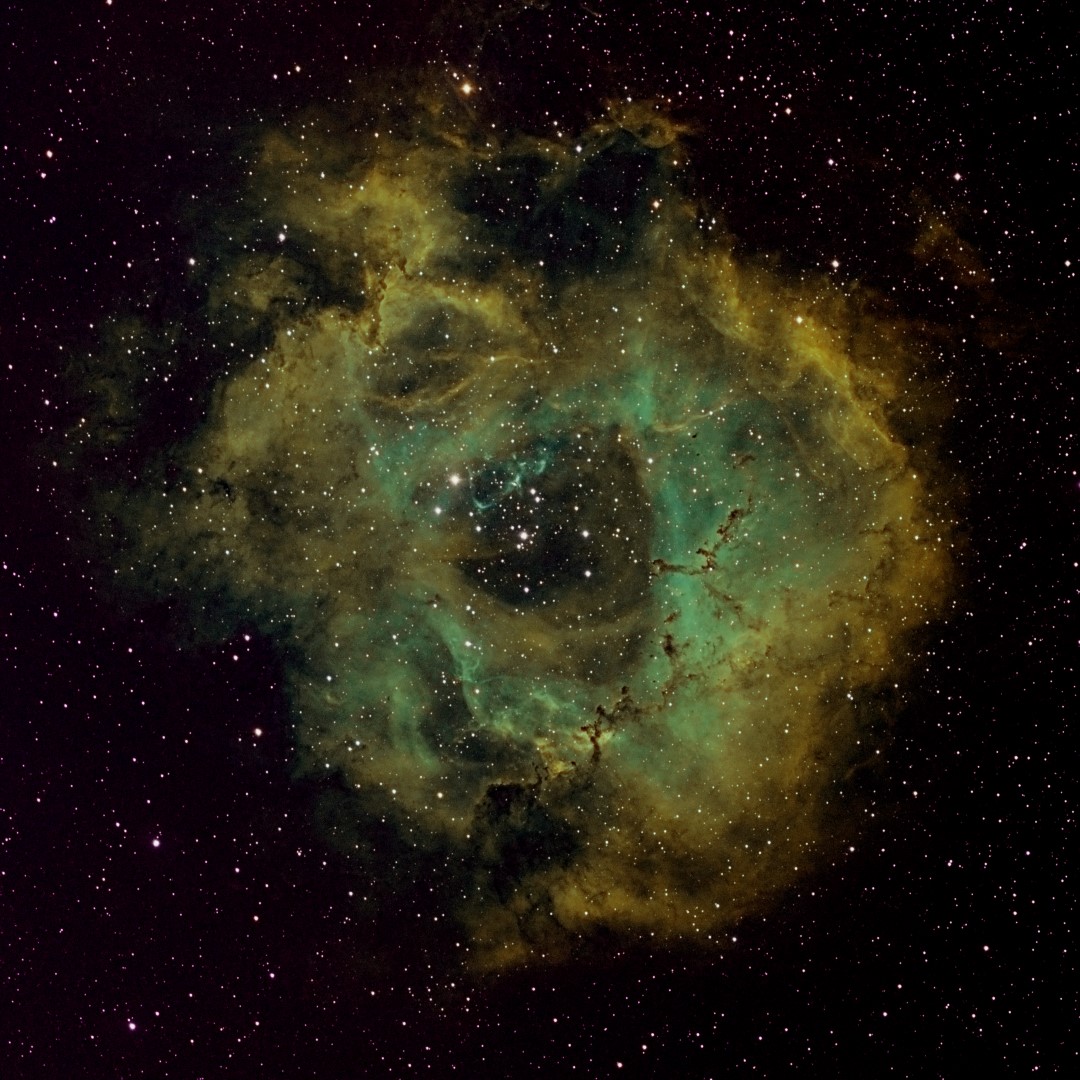



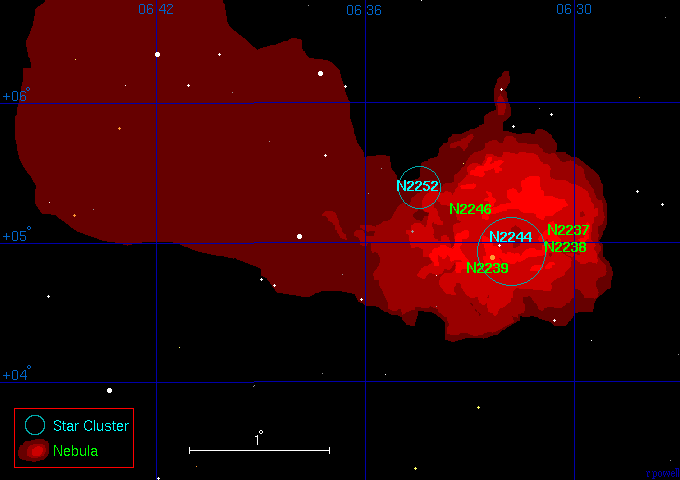


 When the object is right, such as the Rosette Nebula, narrowband imaging using the ZWO camera produces exceptional results. This is evident in these recent images where it’s now possible to clearly see structural elements of the nebula, as well as the star fields located within. Frankly I am very excited by these new images and can’t wait for next year to come around again!
When the object is right, such as the Rosette Nebula, narrowband imaging using the ZWO camera produces exceptional results. This is evident in these recent images where it’s now possible to clearly see structural elements of the nebula, as well as the star fields located within. Frankly I am very excited by these new images and can’t wait for next year to come around again!