I try to ensure that since Watch This Space (Man) blasted off in August 2014, it does what it says on the tin (top of the page): A personal discovery of the Universe through astronomy and astrophotography. Naturally, alongside this journey life goes on, which this year has been a significant challenge for me in many ways. Shortly after imaging the Flaming Star Nebula at Fairvale Observatory, Surrey, in early January, I underwent major surgery to replace my right knee and inevitably, all physical astronomy came to a halt; latterly I managed to remotely obtain and process data from sources in Texas, USA and Chile, which was good fun.
Just two months later, whilst still in early recovery (which can take over a year), serendipity made an unexpected appearance, and by at the end of June, after 40-years living in Redhill, Surrey, we moved to a new house just outside England’s smallest city of Wells (population 11,145), in the beautiful countryside of north Somerset. This upheaval, combined with my recovery, has led to a protracted absence from astrophotography imaging but, at last, I’m now very pleased to present my first image from the new Castle Farm Observatory, in Somerset, of course.
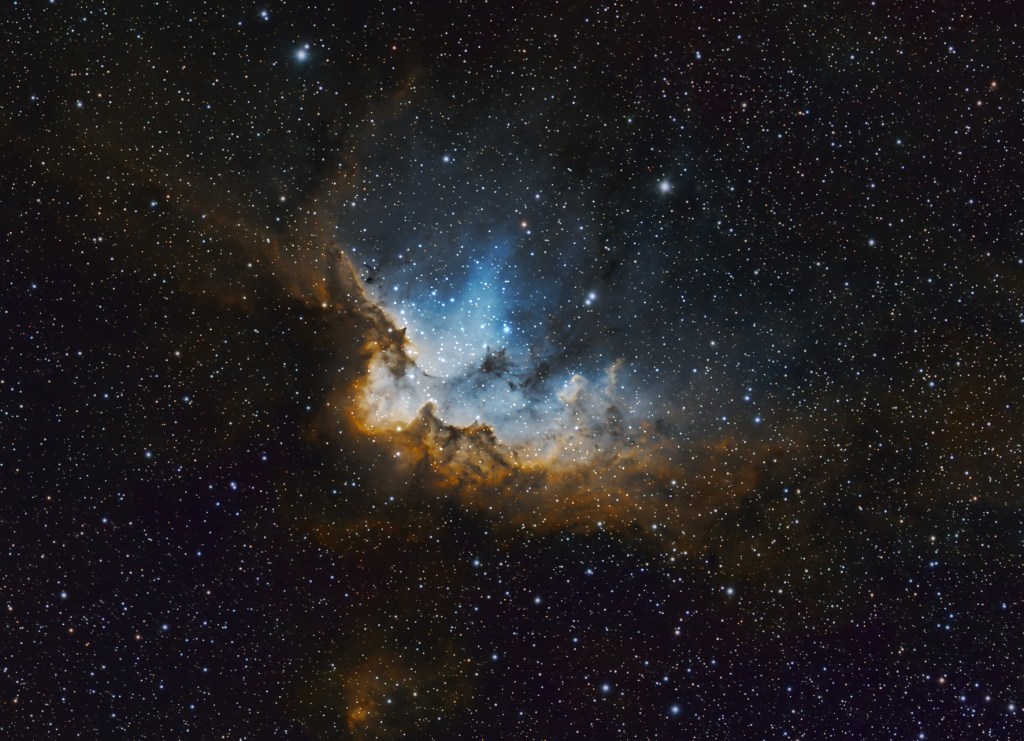
Astronomically speaking, only one thing counts when imaging and that is the quality of viewing conditions (and clear skies), which I can already attest to be excellent here in Somerset. At my previous location just south of London in Surrey, conditions were poor, with an SQM value of 19.82 that was further complicated by low flying aircraft from three nearby airports. In comparison, the SQM at Castle Farm Observatory is 21.11, which being a log scale equates to a difference of x3.28 better sky darkness than before and, moreover, overflying aircraft are no longer a problem. Given this setting, combined with clear skies and a new moon in early September, I had high expectations for my first imaging session since moving to Somerset and was not disappointed by the results obtained of the object chosen for this auspicious occasion, the Wizard Nebula.
The Wizard Nebula, designated by the central star cluster of NGC 7380, is an emission nebula, in which its gases glow due to intense radiation from hot, massive stars from within the aforesaid embedded cluster. Interwoven within this glowing gas are dark, dense regions of dust that sculpt the nebula’s dramatic and somewhat mystical appearance, in this case a wizard. NGC 7380 was only formed a few million years ago and within it, young and massive O- and B-type stars generate strong stellar winds that shape and erode the surrounding material.
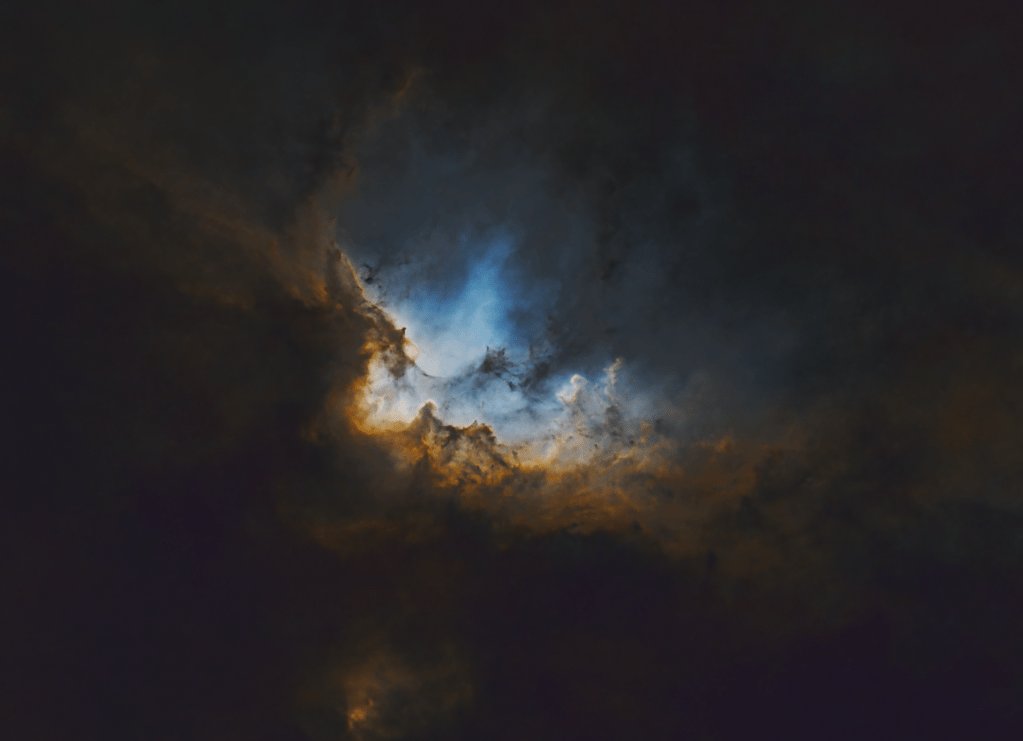

Thus, after an unprecedented break of some 257 days, I’m more than pleased to return to my own backyard astrophotography again, now based in the magic county of Somerset. The quality of the subs obtained on this first occasion confirmed the outstanding sky conditions, which were literally saturated by stars (see starless image above). Altogether, it was significantly better than experienced in Surrey and bodes well for what I hope will be an exciting time here at Castle Farm Observatory – Watch This (new) Space!
| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | NGC 7380 The Wizard Nebula |
| Constellation | Cepheus |
| Distance | >= 7,200 light-years |
| Size | 25 arc minutes (110 light-years) |
| Apparent Magnitude | +7.2 |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount & Control | ZWO AM5 + ASIair |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| + ZWO 120MM Mini | |
| Camera | ZWO ASI294MM CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.87o x 1.96o Resolution 2.50”/pix Max. image size 4,144 x 2,822 pix | |
| EFW | ZWOx8 EFW & 31mm Chroma Ha, OIII, SII 3nm & RGB filters |
| Capture & Processing | ASIair, Deep Sky Stacker & PixInsight v1.9.3 Lockhart |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre = RA 22:47:01.78 DEC +58:02:19.1 Top Left = North |
| Exposures | Ha x 35 + OIII x 35 + SII x 35 @ 300 sec + LRGB x 10 @ 60 sec Total Integration Time: 9hr 15 min |
| @ Gain 120 & 30 Offset 21 @ -15oC | |
| Calibration | 5 x 300 sec & 20 x 60 sec Darks + 10 x NB & 20x BB Flats & Dark Flats @ ADU 32,000 |
| Location & Darkness | Castle Farm Observatory, Wookey, Somerset – UK Typically Bortle 4 |
| Date & Time | 21st & 22nd September 2025 @ +21.00h |
| Weather | Approx. <7oC RH >=<60% 🌙 New Moon |