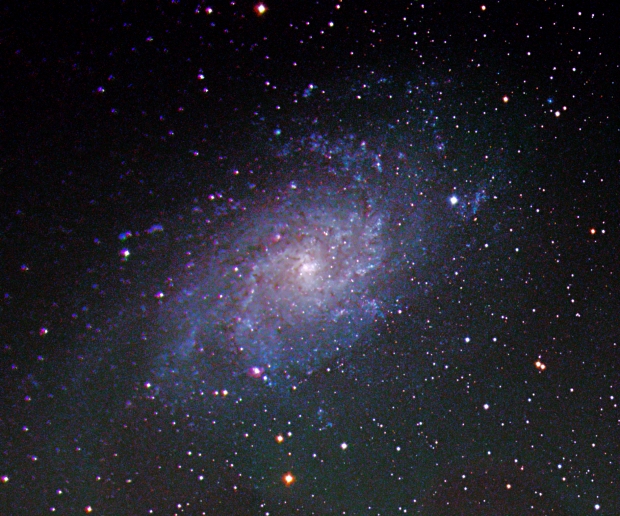

After we say goodbye to Orion each year, the galaxy season starts in February and lasts through until late April. It seems almost unbelievable that the existence of galaxies outside of our own Milky Way was unknown to mankind until Edwin Hubble’s work in 1929; the Andromeda Nebula turned out to be a galaxy as did all those other faint fuzzies and many more that have since been discovered. Like grains of sand on the beach, there are currently known to be at least two trillion galaxies in the observable Universe and no doubt many more as yet remain undiscovered. On Earth we really are a very, very small speck in space and can only wonder at those other worlds.
Despite their abundance I struggle to image galaxies with the otherwise excellent William Optics GT81 telescope, except for the few largest ones that are closest to Earth in the so-called Local Group, such as the aforesaid Andromeda Galaxy and located nearby M33 or the Triangulum Galaxy. About one quarter the size pf Andromeda, M33 still provides a decent imaging target for my equipment, which I’ve attempted before using a DSLR camera with some success. So, before the winter night sky arrives I thought I’d give M33 a try for the first time using the ZWO1600MM-Cool CMOS mono camera.
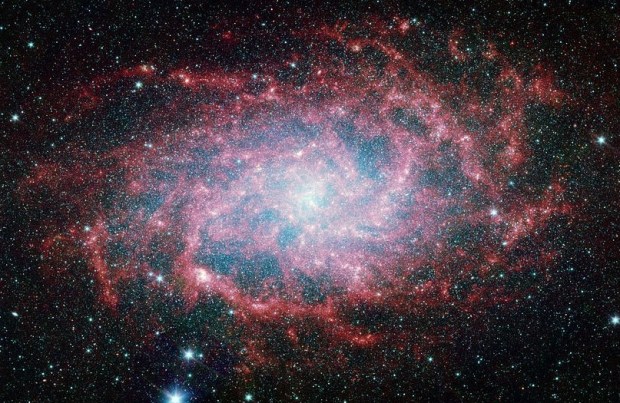
M33 is characterized by its large, sprawling spiral arms, within which are located numerous H-II regions, home to large stellar nurseries. Its mass is thought to extend well beyond the visible galaxy, with large areas of cold dust now identified around and beyond the spiral arms. Interestingly infrared imaging by the Spitzer Space Telescope (below) shows much more discrete structures throughout the disc than is evident in the visible light spectrum. The future of M33 is somewhat uncertain but seems to point towards its destruction, either by Andromeda or alternatively crashing into the Milky Way!
 Imaging experience to-date with the ZWO camera has shown that 5-minute exposures and unitary settings – Gain 139 Offset 21 – produces a good result with most nebulae targets, however, imaging star clusters and galaxies remains work-in-progress. Whilst tempted to continue with this approach, after reviewing and adjusting the PHD2 settings my guiding has been poor recently, so on this occasion I chose shorter 3-minute exposures to obtain LRGB and Ha subs.
Imaging experience to-date with the ZWO camera has shown that 5-minute exposures and unitary settings – Gain 139 Offset 21 – produces a good result with most nebulae targets, however, imaging star clusters and galaxies remains work-in-progress. Whilst tempted to continue with this approach, after reviewing and adjusting the PHD2 settings my guiding has been poor recently, so on this occasion I chose shorter 3-minute exposures to obtain LRGB and Ha subs.
With nearly 3-hours integration time the resulting LRGB image turned out good (top-of-the page) and noticeably better than using a DSLR camera. The H-II regions were captured with the Ha-subs but subsequently did not integrate very well with the main LRGB image – or maybe that was my error? Whilst pleased with the outcome for now, on reflection I think there are issues that still need to be addressed in order to obtain a better outcome next time:
- Although M33 is quite bright, the spiral arms are somewhat diffuse in nature and would benefit from much longer integration time and better guiding to achieve less noise and greater depth in the resulting image;
- The jury’s out on exposure times but I feel that 5-minutes might still work better and is certainly worth trying;
- Though much improved, processing remains a weakness and needs to be improved.
Notwithstanding the above M33 is a wonderful object and, as ever, I remain inspired by the galaxy itself and images of others to do better in the future.
| IMAGING DETAILS | |
| Object | M33 Triangulum Galaxy |
| Constellation | Triangulum |
| Distance | Approx.. 2.7 million light-years |
| Size | 71’ x 42’ or 60,000 light-years |
| Apparent Magnitude | +5.72 |
| Scope | William Optics GT81 + Focal Reducer FL 382mm f4.72 |
| Mount | SW AZ-EQ6 GT + EQASCOM computer control |
| Guiding | William Optics 50mm guide scope |
| + Starlight Xpress Lodestar X2 guide camera & PHD2 control | |
| Camera | ZWO1600MM-Cool (mono) CMOS sensor |
| FOV 2.65o x 2.0o Resolution 2.05”/pix Max. image size 4,656 x 3,520 pix | |
| EFW | ZWOx8 + ZWO LRGB & Ha OIII SII 7nm filters |
| Capture & Processing | Astro Photography Tool + PS2, Deep Sky Stacker & Photoshop CS2, HLVG |
| Image Location & Orientation | Centre RA 01:34:02 DEC 30:38:51
Top = North Right = West Bottom = South Left = East |
| Exposures | 12 x 180 sec RGB + 10×10 sec L & Ha (Total time: 168 minutes) |
| @ 139 Gain 21 Offset @ -20oC | |
| Calibration | 10 x 180 sec Darks 20 x 1/4000 sec Bias 10 x Flats LRGB + Ha @ ADU 25,000 |
| Location & Darkness | Fairvale Observatory – Redhill – Surrey – UK Typically Bortle 5 |
| Date & Time | 9th October 2018 @ +22.00h |
| Weather | Approx. 12oC RH = 90% |

Pingback: Galactic Triplets | WATCH THIS SPACE(MAN)